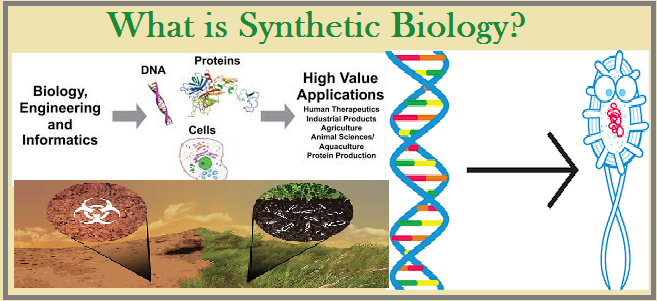
Synthetic biology is a field of biotechnology that combines principles of engineering, chemistry, and biology to create new biological systems with specific functions. The goal is to design, construct, and optimize biological systems that can perform useful tasks, such as producing biofuels, synthesizing drugs, or detecting environmental pollutants. Synthetic biology involves the use of modular DNA parts, called BioBricks, which can be assembled in various combinations to create new genetic circuits and metabolic pathways. This allows researchers to design biological systems with a high degree of precision and predictability.
The promise of synthetic biology lies in its potential to solve some of the world’s most pressing problems, such as climate change, energy security, and food and water shortages. For example, synthetic biology could be used to develop new forms of biofuels that are more efficient and sustainable than traditional fossil fuels. It could also be used to produce new drugs and vaccines that are more effective and less expensive than current treatments. Synthetic biology could even be used to create new materials that are stronger, more flexible, and more sustainable than existing materials.
However, the development and use of synthetic biology also pose significant risks and challenges. One of the main concerns is the potential for unintended consequences. Synthetic biology involves the creation of new biological systems that do not exist in nature, and the interactions between these systems and the natural environment are not well understood. There is a risk that these systems could have unexpected and harmful effects on the environment or human health.
Another concern is the potential for deliberate misuse of synthetic biology. The ability to create new biological systems with specific functions could be used for nefarious purposes, such as creating biological weapons or engineering pathogens for bioterrorism. The rapid advancement of synthetic biology has raised concerns about the need for effective regulation and oversight to ensure that the technology is used responsibly and ethically.
The ethical implications of synthetic biology are also a matter of debate. Some argue that synthetic biology raises fundamental questions about the nature of life and the relationship between humans and the natural world. Others argue that synthetic biology has the potential to enhance human well-being and solve some of the world’s most pressing problems. There is also debate about the ownership and control of synthetic biological systems, and the potential for synthetic biology to exacerbate existing social and economic inequalities.
Despite these challenges and risks, the field of synthetic biology continues to advance rapidly. Many governments and private companies are investing heavily in research and development, and there is a growing community of scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs working to push the boundaries of the field. As synthetic biology continues to evolve, it will be important to ensure that the benefits of the technology are realized while minimizing the risks and addressing the ethical, social, and environmental concerns associated with its development and use.