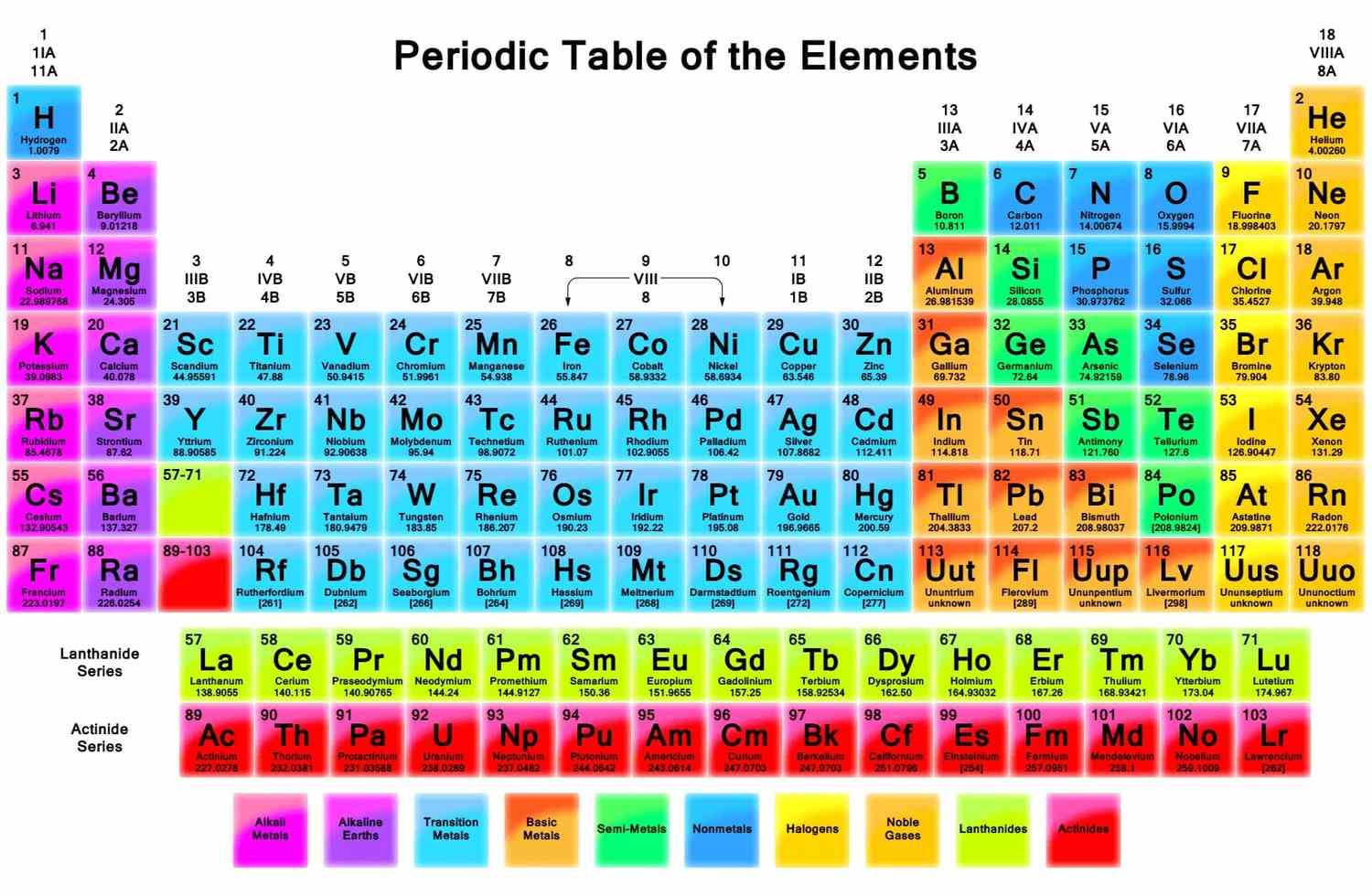
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and chemical properties. It was first proposed by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869 and has since become one of the most important tools in chemistry.
The periodic table is divided into rows and columns, with each row called a period and each column called a group. Elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
The periodic table currently contains 118 elements, with 92 occurring naturally and the rest being synthetic. Each element is represented by a unique symbol and atomic number, which indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
The properties of the elements vary widely. Some elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are gases at room temperature, while others, such as gold and platinum, are metals. Some elements are highly reactive, while others are relatively inert. The properties of the elements can be explained by their electron configurations and their position in the periodic table.
The elements in the periodic table can be classified into several categories based on their properties. These categories include metals, nonmetals, metalloids, noble gases, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and transition metals. Each category has unique properties and applications in various fields.
Metals are elements that are generally shiny, malleable, and good conductors of heat and electricity. They make up the majority of the periodic table and have a wide range of applications, from construction and manufacturing to electronics and aerospace.
Nonmetals are elements that lack the metallic properties of metals. They are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity and have low melting and boiling points. Nonmetals include elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, which are essential for life.
Metalloids are elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals. They are semiconductors, meaning they can conduct electricity under certain conditions but not under others. Metalloids include elements such as silicon, which is used in the manufacture of computer chips.
Noble gases are elements that are generally unreactive and exist as gases at room temperature. They are used in various applications, including lighting, welding, and cryogenics.
Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals are highly reactive metals that are important in various chemical reactions. They have a wide range of applications, from the production of fertilizers and batteries to the synthesis of new materials.
Halogens are elements that are highly reactive and form salts with metals. They have a wide range of applications, from water treatment and disinfection to the production of plastics and pharmaceuticals.
Transition metals are elements that have partially filled d-orbitals and exhibit a wide range of oxidation states. They have a wide range of applications, from catalysis and electronics to medicine and agriculture.
In conclusion, the periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry that provides a comprehensive guide to the elements. It organizes the elements based on their atomic structure and properties, allowing scientists to understand and predict the behavior of matter. With its wide range of applications in various fields, the periodic table continues to play a vital role in the advancement of science and technology.