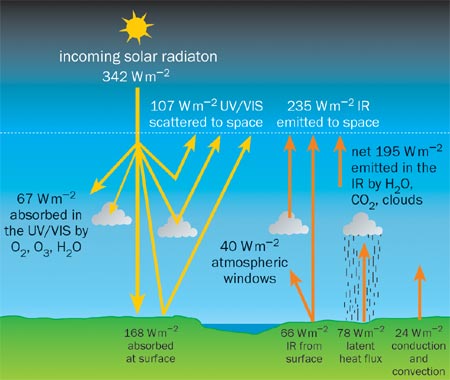
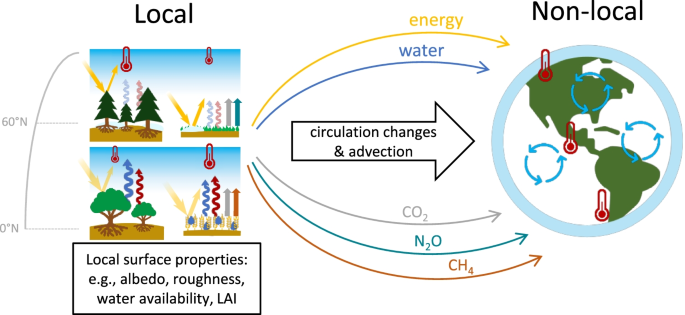
Introduction:
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and its consequences are being felt across the globe. While the causes of climate change are multifaceted, one significant contributor often overlooked is agriculture. The way we produce our food, manage our land, and raise livestock has a profound impact on the environment. In this blog post, we will uncover the intricate relationship between agriculture and climate change, shedding light on the various ways in which farming practices influence our planet’s climate. We will also explore how sustainable agriculture can play a pivotal role in mitigating these effects.
Agriculture and Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
At the heart of the connection between agriculture and climate change are greenhouse gas emissions. Agriculture is a major source of these gases, particularly methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O), both of which are potent contributors to global warming.
Methane Emissions: Livestock, such as cattle, sheep, and goats, produce methane during digestion through a process called enteric fermentation. Additionally, manure management and rice cultivation release substantial amounts of methane into the atmosphere. Methane is over 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide (CO2), making it a significant concern.
Nitrous Oxide Emissions: Nitrous oxide is released primarily from agricultural activities like the use of synthetic fertilizers and the management of livestock manure. This greenhouse gas is nearly 300 times more potent than CO2 in terms of its heat-trapping ability.
Deforestation and Land Use Change:
Agriculture also drives deforestation and land use changes, contributing to climate change in multiple ways:
Deforestation: To make way for agricultural expansion, large areas of forests are cleared. This not only releases carbon stored in trees into the atmosphere but also reduces the planet’s capacity to absorb CO2. Forests act as carbon sinks, and their destruction exacerbates global warming.
Land Degradation: Unsustainable farming practices, such as overgrazing and excessive use of chemicals, can lead to land degradation. This diminishes the land’s ability to sequester carbon and maintain ecosystem balance.
The Energy Intensive Nature of Agriculture:
Modern agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels. Tractors, irrigation systems, transportation, and the production of synthetic fertilizers all require significant energy inputs. These processes release CO2 into the atmosphere and contribute to climate change. The carbon footprint of food production extends beyond the farm and into every aspect of the agricultural supply chain.
Water Use and Climate Change:
Agriculture is a major consumer of freshwater resources. As the climate changes, weather patterns become more unpredictable, leading to increased droughts and water scarcity in many regions. This puts additional pressure on agriculture, as farmers need to adapt their practices, often requiring more water-intensive methods. The cycle of increased water demand exacerbates climate change through energy-intensive water pumping and irrigation.
Sustainable Agriculture as a Solution:
While agriculture plays a significant role in climate change, it can also be part of the solution. Sustainable farming practices aim to minimize the negative environmental impacts of agriculture while still providing food security. Here are some ways in which sustainable agriculture can contribute to climate change mitigation:
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Sustainable farming methods, such as organic farming, agroforestry, and rotational grazing, can reduce methane and nitrous oxide emissions. These methods prioritize soil health, reduce the use of synthetic fertilizers, and promote practices that sequester carbon.
Conservation and Reforestation: Sustainable agriculture often incorporates practices that protect existing forests, promote reforestation, and enhance biodiversity. These actions can help offset emissions and preserve valuable carbon sinks.
Efficient Resource Use: Sustainable agriculture focuses on optimizing resource use, including water and energy. Precision agriculture techniques, for example, allow farmers to use resources more efficiently, reducing the carbon footprint of food production.
Climate-Resilient Crops: Developing and planting crops that are more resilient to changing climate conditions can help ensure food security in the face of extreme weather events.
Conclusion:
The influence of agriculture on climate change cannot be understated. From greenhouse gas emissions to deforestation, from energy-intensive practices to water use, agriculture has far-reaching effects on our planet’s climate. However, it’s important to recognize that agriculture can also be a part of the solution. Embracing sustainable farming practices is crucial in mitigating the negative impacts of agriculture on climate change. As consumers, policymakers, and farmers, we all have a role to play in shaping a more sustainable and climate-resilient food system. The choices we make today will determine the future of our planet’s climate.