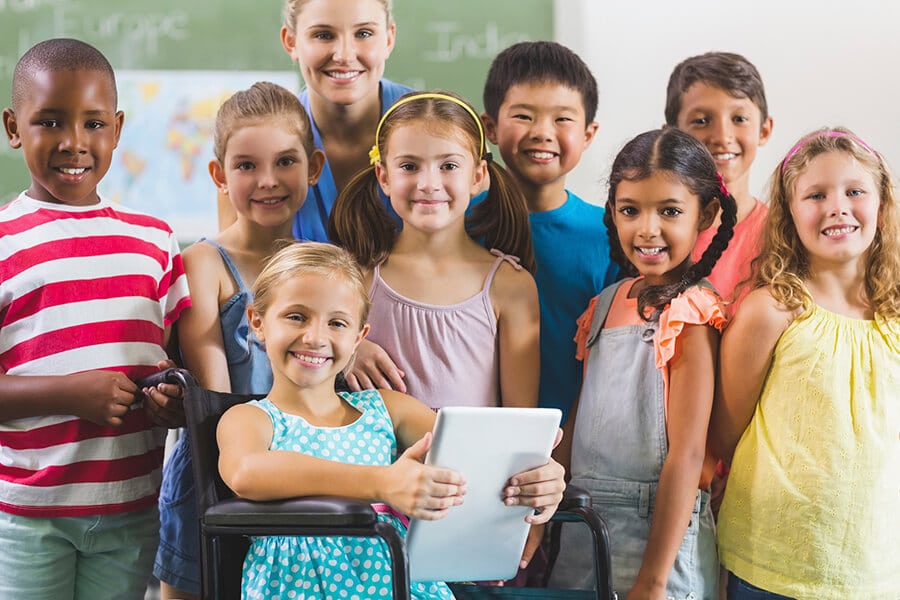
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on inclusion in special education. Inclusion refers to the practice of integrating students with disabilities into regular classrooms and providing them with the support and accommodations they need to succeed academically and socially.
There are several reasons why inclusion is important in special education. First, inclusion can promote greater understanding and acceptance of diversity among students. When students with disabilities are included in regular classrooms, their non-disabled peers have the opportunity to interact with them and learn about their unique strengths and challenges.
Second, inclusion can help students with disabilities develop stronger social and communication skills. By interacting with their non-disabled peers, students with disabilities can learn important social skills such as communication, cooperation, and empathy. They can also develop a greater sense of self-esteem and belonging, which can contribute to their overall success in school and beyond.
Third, inclusion can improve academic outcomes for students with disabilities. When students with disabilities are included in regular classrooms, they have access to the same curriculum and instruction as their non-disabled peers. They also have the opportunity to participate in group activities and projects, which can enhance their learning and social skills.
Inclusion can also benefit non-disabled students. Research has shown that inclusion can promote greater acceptance and understanding of diversity among non-disabled students. It can also improve their academic and social skills by providing opportunities for collaboration and learning from their peers with disabilities.
Despite the many benefits of inclusion, there are still some challenges to implementing it effectively. One of the biggest challenges is providing the necessary support and accommodations to students with disabilities. Teachers need to be trained in how to modify their instruction and provide accommodations to meet the diverse needs of their students.
Another challenge is addressing the attitudes and beliefs of some teachers and parents who may not be fully supportive of inclusion. Some teachers may feel that they lack the necessary skills or resources to effectively teach students with disabilities, while some parents may have concerns about the impact of inclusion on their child’s academic and social development.
To address these challenges, it is important to provide ongoing training and support to teachers and to involve parents and caregivers in the inclusion process. Teachers can benefit from professional development opportunities that provide them with the knowledge and skills they need to effectively support students with disabilities. Parents and caregivers can also play a key role in advocating for their child’s needs and supporting their participation in inclusive environments.
In conclusion, inclusion is a vital aspect of special education that benefits both students with disabilities and their non-disabled peers. By promoting greater understanding and acceptance of diversity, improving social and communication skills, and enhancing academic outcomes, inclusion can help all students reach their full potential. While there are challenges to implementing inclusion effectively, with the right support and resources, it is possible to create inclusive learning environments that support the success of all students.