Introduction
Agriculture is the backbone of human civilization, providing sustenance and livelihoods for billions of people across the globe. From the rice fields of Southeast Asia to the cornfields of the American Midwest, crops are cultivated with care and dedication. However, the journey of these crops from the farm to the fork is not as straightforward as it may seem. One critical aspect that often goes overlooked is crop storage and preservation.
In an era where food security, sustainability, and reducing food wastage are paramount, understanding the importance of crop storage and preservation is crucial. In this blog post, we will explore this often-underestimated facet of agriculture and delve into its significance in today’s world.
The Role of Crop Storage
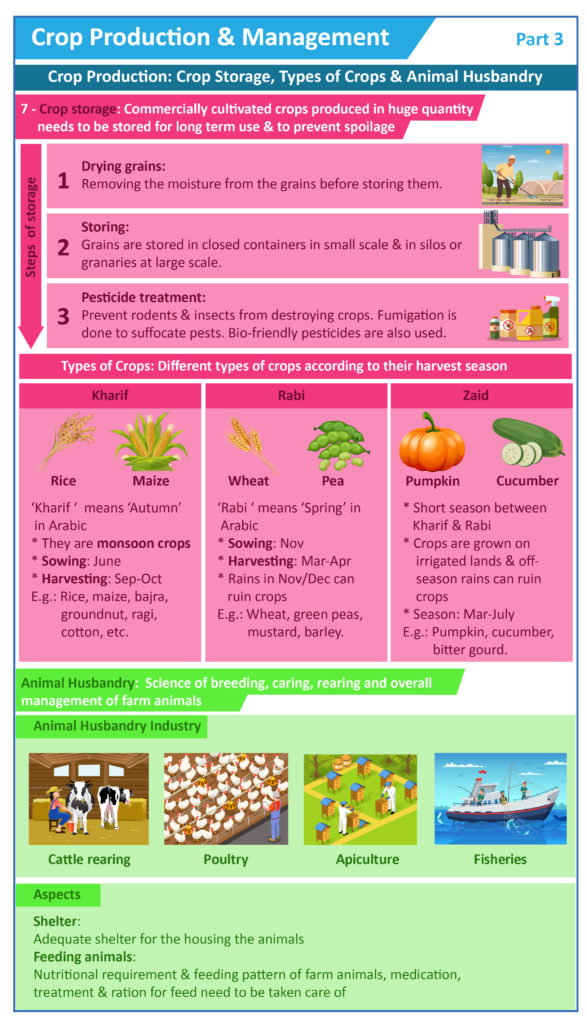
Crop storage refers to the methods and facilities used to store harvested crops for an extended period. This phase of agriculture is often underrated, as most of the attention is focused on planting, growing, and harvesting. However, crop storage is the bridge that connects the efforts of farmers to the plates of consumers.
Ensuring Food Security
One of the primary reasons for the importance of crop storage is its direct impact on food security. Food security is the condition in which all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. Achieving food security is not just about producing crops; it’s about preserving them effectively.
Proper crop storage prevents post-harvest losses due to spoilage, pests, and diseases. In many parts of the world, particularly in developing countries, inadequate storage facilities can lead to significant crop losses. This, in turn, affects the availability of food, leading to scarcity and higher prices. Crop storage ensures that surplus crops can be stored and distributed throughout the year, reducing the vulnerability of communities to food shortages.
Reducing Food Wastage
Food wastage is a global concern that not only impacts food security but also has severe environmental and economic consequences. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally. This is where crop preservation comes into play.
Proper preservation methods such as drying, canning, and freezing can significantly extend the shelf life of crops. By preventing spoilage and decay, these methods reduce the amount of food that ends up in landfills. Moreover, they enable farmers to sell their produce when prices are favorable, rather than being forced to sell immediately after harvest due to storage constraints.
Sustaining Agricultural Communities
In many rural areas, agriculture is the primary source of income for families and communities. The ability to store crops effectively can have a profound impact on the livelihoods of these agricultural communities. When farmers can store their crops and sell them strategically, they can negotiate better prices and improve their overall economic well-being.
Additionally, crop storage can help bridge the gap between harvest seasons. In regions with distinct growing seasons, having access to stored crops can provide a consistent income throughout the year, reducing the vulnerability of farmers to seasonal fluctuations.
The Importance of Crop Preservation
Crop preservation goes hand in hand with storage, as it involves methods to maintain the quality and nutritional value of crops over time. Here’s why crop preservation matters:
Retaining Nutritional Value
When crops are harvested, they begin to lose their nutritional value over time. Vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients degrade if not preserved properly. By using preservation techniques like freezing or canning, it’s possible to lock in the nutritional content of crops, ensuring that consumers receive the maximum benefit from the food they consume.
Extending Shelf Life
Preservation methods not only retain nutritional value but also extend the shelf life of crops. This is particularly important for perishable fruits and vegetables. A longer shelf life means less waste and more time for consumers to enjoy the produce.
Enabling Long-Distance Transportation
Modern food systems often involve the transportation of crops over long distances. Without proper preservation, many crops would not survive the journey from farm to market. Preservation methods, such as refrigeration and vacuum packing, allow for the safe transport of crops, enabling consumers to access a wider variety of foods.
Conclusion
Crop storage and preservation may not always be in the spotlight, but their importance cannot be overstated. They are the unsung heroes of agriculture, ensuring that the hard work of farmers reaches the tables of consumers. By reducing food wastage, improving food security, and sustaining agricultural communities, these practices play a vital role in creating a more resilient and sustainable food system.
As consumers, we can also contribute to the cause by being mindful of food wastage at our end and supporting initiatives that promote proper crop storage and preservation. Together, we can work towards a world where no one goes to bed hungry, and where the fruits of our agricultural labor are cherished and utilized to their fullest potential.