Introduction:
Pesticides, a broad category of chemicals designed to kill or control pests that harm crops and livestock, have played a pivotal role in modern agriculture. They have significantly increased crop yields, reduced post-harvest losses, and helped safeguard food security. However, this convenience comes at a cost. The excessive and often indiscriminate use of pesticides has raised alarm bells regarding their detrimental effects on the environment and human health. In this article, we will unravel the intricate web of pesticide usage, discussing the various ways they impact our planet and our well-being.
The Widespread Use of Pesticides:
Pesticides come in various forms, including insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, each designed to combat specific types of pests. Farmers and agricultural producers have embraced these chemical agents as effective tools to protect their crops and maximize yields. The allure of higher profits and increased productivity has led to the widespread and often intensive use of pesticides in modern agriculture. This dependence, however, has resulted in numerous unintended consequences.
Environmental Impact:
1: Biodiversity
2: Water Pollution
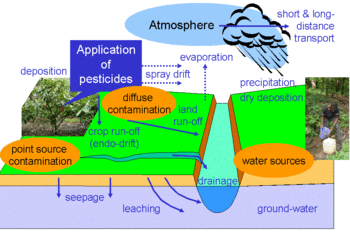
The environmental impact of pesticides is a cause for significant concern. When pesticides are applied to crops, they don’t discriminate between harmful pests and beneficial insects, such as pollinators like bees and butterflies. This collateral damage can disrupt ecosystems and harm biodiversity. Additionally, pesticides can leach into the soil and contaminate groundwater, leading to long-lasting environmental damage. The runoff from fields can also enter nearby water bodies, causing water pollution and harming aquatic life.
Human Health Concerns:
3: Public Health
4: Food Safety
The consequences of pesticide exposure extend beyond the environment to human health. Farmworkers, who are often in close proximity to pesticide application, are at particular risk. Pesticides can lead to acute and chronic health issues, ranging from skin irritations and respiratory problems to more severe conditions like cancer and neurological disorders. Residues of these chemicals can also make their way into the food supply, posing a threat to consumers’ health. Ensuring food safety and protecting public health are paramount concerns.
Alternatives and Sustainable Practices:
1: Organic Farming
2: Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
In light of the environmental and health risks associated with pesticides, many farmers and agricultural experts are exploring alternative methods. Organic farming, for instance, emphasizes natural pest control and avoids synthetic pesticides. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) combines multiple strategies, such as crop rotation and the use of beneficial insects, to reduce the need for chemical pesticides. These sustainable practices not only minimize harm but also promote long-term agricultural resilience.
Government Regulations and Consumer Awareness:
3: Regulation
4: Consumer Choices
Government regulations play a crucial role in mitigating the negative effects of pesticides. Strict guidelines can help limit the use of harmful chemicals and protect both the environment and public health. Furthermore, consumer awareness and demand for pesticide-free products have led to changes in the agricultural industry. As consumers become more informed about the potential risks, they can make choices that support sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices.
Conclusion:
Pesticides have undeniably revolutionized agriculture and contributed to increased food production. However, their indiscriminate use has led to significant repercussions for the environment and human health. It is imperative that we strike a balance between the benefits and drawbacks of pesticides, exploring alternative, sustainable practices while advocating for stricter regulations. By doing so, we can ensure a healthier, more sustainable future for our planet and ourselves.