Introduction:
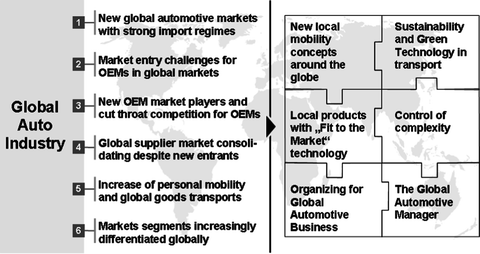
Globalization, the process of increased interconnectedness and interdependence among countries and their economies, has left an indelible mark on almost every aspect of our lives. One industry that has experienced significant transformation due to globalization is car manufacturing. Gone are the days when automobiles were predominantly produced and consumed within the boundaries of a single country. Today, cars are the epitome of a globalized industry, with components sourced from multiple countries, assembly plants scattered across continents, and a consumer base that spans the globe.
In this blog post, we will explore the multifaceted impact of globalization on car manufacturing. From supply chain dynamics to the ever-expanding consumer choices, and the environmental implications of this globalized industry, we will delve deep into how globalization has reshaped the automotive landscape.
Tag 1: Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is the epicenter of globalization’s impact, with far-reaching consequences for both producers and consumers.
Tag 2: Supply Chain
Globalization has profoundly altered the supply chain dynamics in car manufacturing, resulting in more complex and far-reaching networks.
Tag 3: Consumer Choices
Consumers today enjoy a wider array of choices in automobiles, thanks to globalization’s influence on product diversity.
Tag 4: Environmental Impact
Globalization has raised critical questions about the environmental sustainability of car manufacturing and its implications for the planet.
The Globalized Supply Chain:
One of the most noticeable impacts of globalization on car manufacturing is the transformation of the supply chain. Traditionally, car manufacturers sourced a significant portion of their components and materials locally. However, globalization has led to the dispersion of suppliers across the world, as manufacturers seek cost-effective solutions and specialized expertise.
Today, a single car can contain parts manufactured in different countries and assembled in yet another. This global supply chain has enabled manufacturers to optimize costs and access specialized components, but it has also made supply chains vulnerable to disruptions, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic when border closures and lockdowns disrupted the flow of essential components.
Consumer Choices and Globalization:
Globalization has brought about a revolution in consumer choices when it comes to automobiles. In the past, consumers in a particular country had limited exposure to cars from other regions. Today, thanks to globalization, consumers can choose from a vast array of vehicles, each catering to different tastes, preferences, and needs.
For example, Japanese automakers have gained popularity for their reliable and fuel-efficient cars, while European manufacturers are known for their luxury and performance-oriented vehicles. Meanwhile, American automakers continue to produce iconic pickup trucks and SUVs. This diversity of choice is a direct result of globalization, as manufacturers adapt their offerings to suit different markets around the world.
Environmental Implications:
While globalization has brought undeniable benefits to car manufacturing, it has also raised significant environmental concerns. The increased transportation of components and finished vehicles across long distances has led to a spike in carbon emissions. Additionally, the drive for cost-efficiency often prioritizes the use of fossil fuels in manufacturing and transportation, exacerbating the industry’s carbon footprint.
To address these concerns, many automakers are now embracing sustainability initiatives, such as electric vehicle (EV) production and the adoption of renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities. These efforts are aimed at mitigating the environmental impact of globalized car manufacturing.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Globalization has presented both challenges and opportunities for the car manufacturing industry. On the one hand, the complex global supply chain can be vulnerable to disruptions, as demonstrated by the pandemic. On the other hand, it has allowed manufacturers to tap into diverse markets, reduce costs, and access specialized expertise.
Moreover, globalization has driven innovation and competitiveness in the industry. The need to stay ahead in the global market has led to advancements in technology, safety features, and sustainability practices. Competition among manufacturers from different regions has pushed them to innovate and provide better value to consumers.
Conclusion:
The impact of globalization on car manufacturing cannot be overstated. From the transformation of supply chain dynamics to the diversification of consumer choices and the imperative to address environmental concerns, globalization has left an indelible mark on the industry.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve in response to globalization, it faces both challenges and opportunities. It must navigate the complexities of a global supply chain while embracing sustainability practices and meeting the diverse preferences of consumers worldwide. In this globalized era, the future of car manufacturing lies in innovation, adaptability, and a commitment to a more sustainable and interconnected world.