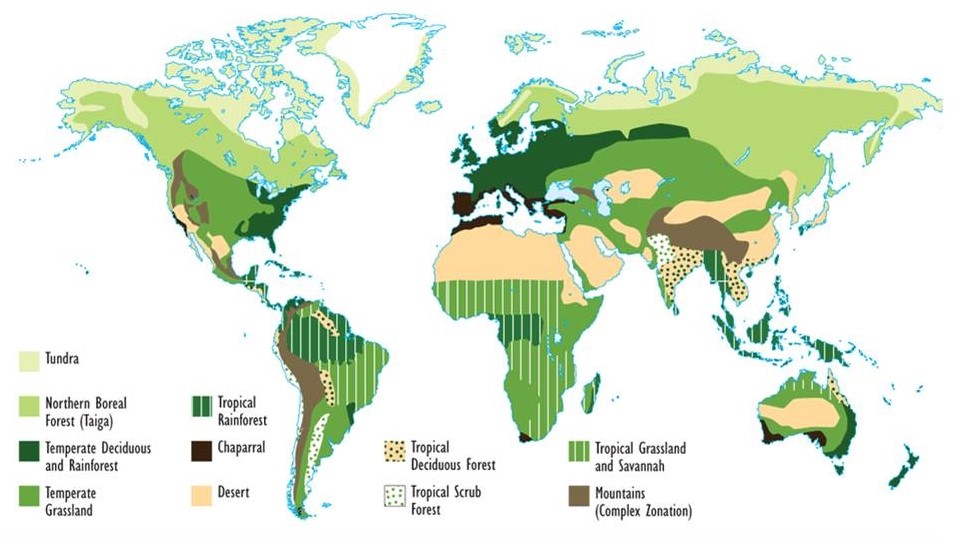
Introduction:
Biomes are large regions of the world with similar climates, flora, and fauna. Ecosystems, on the other hand, are smaller communities of plants and animals that interact with each other and their physical environment. Both biomes and ecosystems are essential components of the Earth’s biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life on our planet.
Tropical Rainforest Biome:
Tropical rainforests are found near the equator and are characterized by high temperatures, humidity, and rainfall. They are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, including toucans, jaguars, and the world’s largest butterfly, the Queen Alexandra’s birdwing. The rainforest biome is also a vital carbon sink and plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
Desert Biome:
Deserts are defined as areas that receive less than 10 inches of rainfall per year. They are characterized by extreme temperatures, aridity, and sparse vegetation. Despite their harsh conditions, deserts are home to a variety of animals such as camels, snakes, and scorpions, many of which have unique adaptations to help them survive in this environment.
Grassland Biome:
Grasslands are vast areas of land dominated by grasses, with few trees or shrubs. They are found on every continent except Antarctica and are home to a variety of animals such as zebras, gazelles, and bison. Grasslands are also important for agriculture and are used for grazing livestock and growing crops such as wheat and corn.
Aquatic Ecosystems:
Aquatic ecosystems include both freshwater and marine environments and are home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. Coral reefs, for example, are a type of marine ecosystem that support a variety of fish and invertebrates. Freshwater ecosystems, such as rivers and lakes, are home to fish, amphibians, and reptiles, as well as a variety of plant life.
Conservation and Biodiversity:
The Earth’s biomes and ecosystems are under threat from human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. Protecting biodiversity is essential for maintaining the health of our planet’s ecosystems and ensuring the survival of many plant and animal species. Conservation efforts such as habitat restoration, protected areas, and sustainable resource management are crucial for maintaining the diversity of life on Earth.
Conclusion:
The world’s biomes and ecosystems are fascinating and diverse, each with its unique characteristics and adaptations. From rainforests to deserts, grasslands to aquatic ecosystems, there is much to explore and appreciate. Protecting biodiversity and preserving these ecosystems is vital for the health of our planet and the survival of many species.