Introduction
In the world of agriculture and gardening, there’s a growing buzz about cover crops and their remarkable benefits for soil health. Cover crops, often referred to as “green manure,” are plants that are grown not for harvest, but to cover and protect the soil. They’ve been gaining popularity among farmers and gardeners alike for their ability to improve soil quality, reduce erosion, enhance biodiversity, and contribute to more sustainable farming practices. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of cover crops and explore why they are becoming an essential component of modern agriculture.
The Basics of Cover Crops
Before delving into their benefits, it’s important to understand what cover crops are and how they work. Cover crops are typically sown in between regular crop rotations or during fallow periods when the field would otherwise be left bare. These crops serve a multitude of purposes:
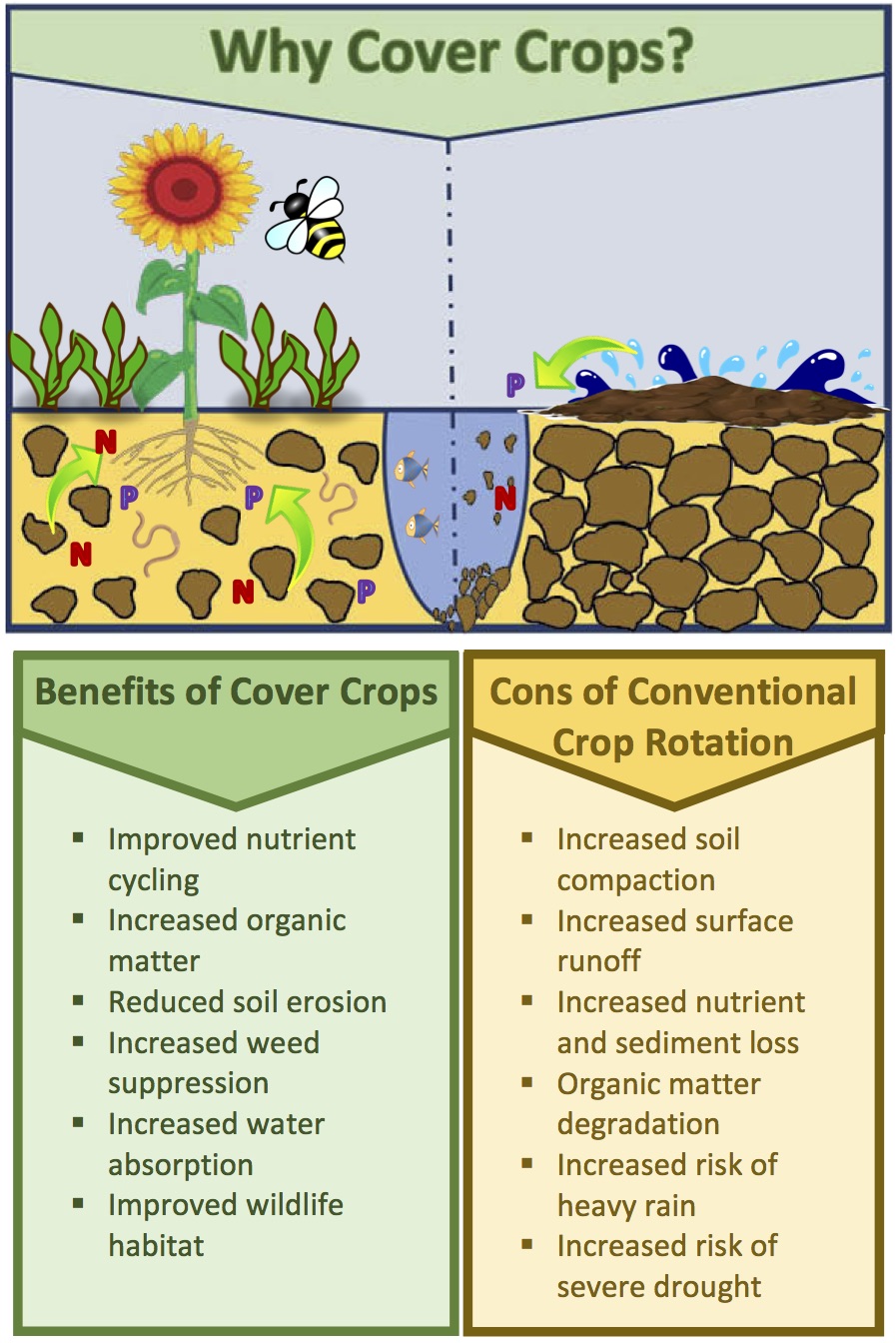
Soil Protection: Cover crops act as a protective blanket for the soil. Their dense growth shades the ground, reducing the impact of harsh weather conditions such as heavy rains and extreme temperatures.
Erosion Prevention: The root systems of cover crops help bind soil particles together, preventing erosion caused by wind and water. This is particularly crucial on sloping fields prone to runoff.
Weed Suppression: Cover crops outcompete weeds for resources like sunlight and nutrients, effectively reducing weed growth and the need for herbicides.
Nutrient Management: Certain cover crops, like legumes, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, making it more accessible to subsequent crops. This reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Biodiversity Enhancement: Cover crops can attract beneficial insects and pollinators, contributing to enhanced biodiversity on the farm.
Benefits of Cover Crops for Soil Health
Now that we have a grasp of what cover crops are and their basic functions, let’s explore the myriad benefits they offer for soil health:
Improved Soil Structure
One of the most significant advantages of cover crops is their ability to enhance soil structure. Their root systems break up compacted soil, allowing for better water infiltration and aeration. This, in turn, promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms, which further contribute to soil health.
Increased Organic Matter
As cover crops grow and eventually decompose, they add organic matter to the soil. This organic matter improves soil fertility, water retention, and nutrient-holding capacity. It’s like nature’s way of providing a slow-release fertilizer to the land.
Nitrogen Fixation
Legume cover crops, such as clover and vetch, have the remarkable ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use. This nitrogen-fixing process reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which can have negative environmental impacts.
Weed Control
Cover crops, with their rapid growth and shading effect, outcompete weeds for resources. This natural weed suppression reduces the need for herbicides, promoting healthier and less chemically dependent farming practices.
Erosion Control
Cover crops are excellent erosion fighters. Their roots hold soil in place, preventing it from being washed away by rain or blown away by wind. This is particularly vital in regions with hilly or sloping terrain.
Pest and Disease Management
Some cover crops release compounds that can deter or suppress pests and soil-borne diseases. This can reduce the reliance on pesticides, benefiting both the environment and human health.
Increased Biodiversity
Cover crops can attract beneficial insects like pollinators and natural predators of crop-damaging pests. This enhanced biodiversity contributes to a healthier, more balanced ecosystem within the farm.
Extended Growing Seasons
In some regions, cover crops can extend the growing season by protecting the soil from frost. This allows for earlier planting in the spring, leading to higher crop yields.
Climate Resilience
With climate change bringing more extreme weather events, cover crops can help mitigate their effects. They act as a buffer against heavy rains, floods, and droughts, reducing soil erosion and improving overall resilience.
Cost Savings
While there may be initial costs associated with planting and managing cover crops, the long-term benefits often outweigh these expenses. Reduced reliance on synthetic inputs like fertilizers and herbicides can lead to significant cost savings for farmers.
Conclusion
Cover crops are a sustainable agricultural practice that offers a multitude of benefits for soil health. From improving soil structure to reducing erosion, enhancing biodiversity, and promoting sustainable farming, cover crops are a win-win for both the environment and farmers. As we face increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable farming practices, cover crops are emerging as a valuable tool in our quest to protect and rejuvenate the soil that sustains us. So, whether you’re a large-scale farmer or a backyard gardener, consider integrating cover crops into your planting rotation and witness the positive impact on your soil’s health and productivity.