Introduction
The universe has always been a subject of intrigue, inspiring humans to gaze at the night sky in wonder for millennia. Over the centuries, astronomers and astrophysicists have developed increasingly sophisticated tools to study the cosmos. However, in recent years, a new player has emerged on the scene: quantum sensors. These cutting-edge devices, hailing from the world of quantum physics, have the potential to revolutionize the way we observe and understand the universe.
The Quantum Revolution
Before we dive into the applications of quantum sensors in astronomy and astrophysics, let’s take a moment to understand what makes them so unique. At their core, quantum sensors harness the principles of quantum mechanics, a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the smallest scales. Unlike classical sensors, which operate based on classical physics, quantum sensors leverage quantum properties such as superposition and entanglement to achieve unprecedented levels of precision and sensitivity.
Applications in Astronomy
- Gravitational Wave Detection
One of the most groundbreaking applications of quantum sensors in astronomy is their role in detecting gravitational waves. Gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime itself, generated by the acceleration of massive objects like merging black holes or neutron stars. Traditional detectors, such as LIGO and Virgo, have already made historic discoveries by measuring these waves, but quantum sensors promise to take this field to new heights.
Quantum-enhanced interferometers, for example, can significantly improve the sensitivity of gravitational wave detectors. These sensors utilize the superposition of quantum states to enhance the measurement of minute spacetime distortions caused by passing gravitational waves. This increased sensitivity enables scientists to detect even fainter signals, unlocking a deeper understanding of the universe’s most enigmatic phenomena.
- Dark Matter Detection
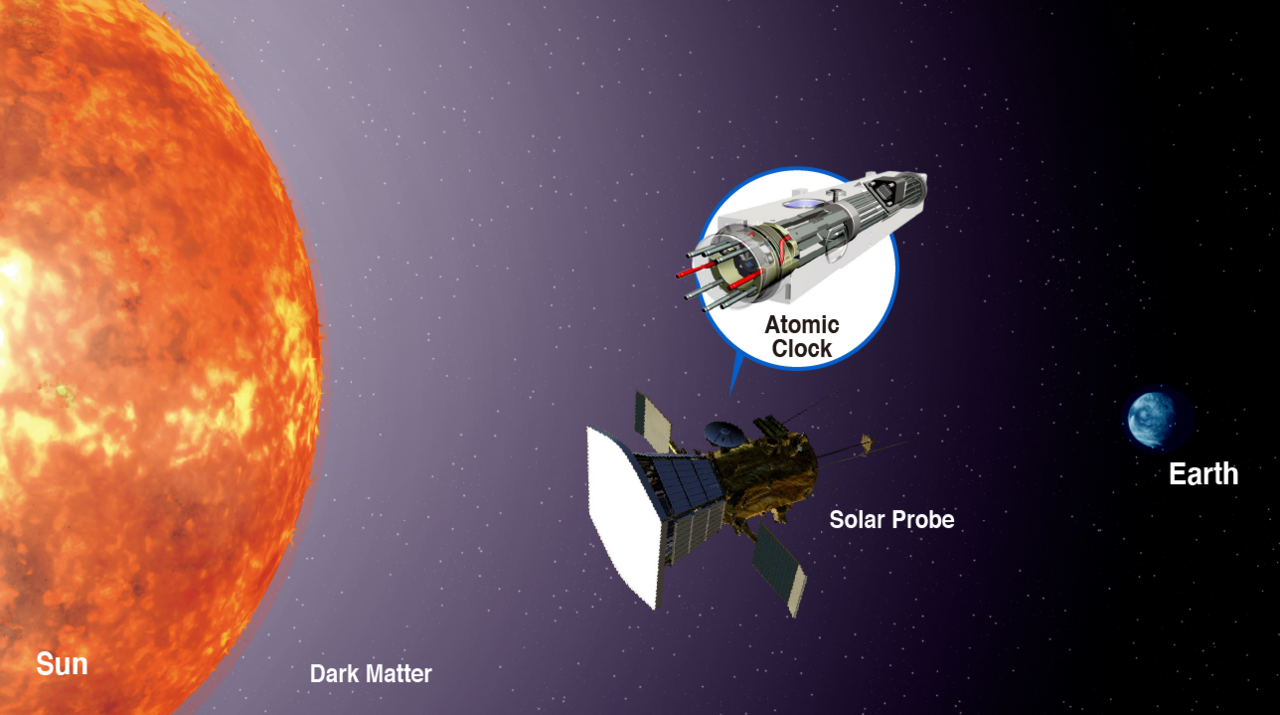
Dark matter, a mysterious and invisible substance that makes up a significant portion of the universe’s mass, has long baffled astrophysicists. Detecting dark matter particles directly has proven to be an elusive quest, but quantum sensors offer a glimmer of hope. Some quantum sensors can be employed in experiments aimed at detecting the elusive dark matter particles by measuring their gravitational interactions with visible matter.
These sensors, based on the delicate interplay between quantum states and gravitational forces, have the potential to reveal the presence and properties of dark matter, shedding light on one of the most perplexing mysteries of the cosmos.
Applications in Astrophysics
- Quantum Imaging
In the field of astrophysics, capturing detailed images of distant celestial objects is essential for studying their properties and evolution. Quantum sensors are enhancing our ability to obtain high-resolution images of astronomical phenomena, such as distant galaxies and black holes.
Quantum-enhanced imaging techniques, like quantum ghost imaging and quantum-enhanced telescopes, are pushing the boundaries of what was once thought possible. These methods leverage the quantum properties of entanglement to improve image resolution, allowing scientists to peer deeper into the universe and observe celestial objects with unprecedented clarity.
- Quantum Clocks for Precision Timing
Astrophysical observations often require precise timing. Whether measuring the rotational periods of pulsars or coordinating observations of astronomical events, accurate timekeeping is crucial. Quantum sensors are now entering the arena of precision timing with the development of quantum clocks.
Quantum clocks, which rely on the oscillations of quantum particles, offer unrivaled stability and accuracy. These clocks can provide precise timekeeping over long durations, making them invaluable tools for astrophysical observations and experiments.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While quantum sensors hold immense promise for astronomy and astrophysics, they are not without their challenges. Technical hurdles, such as maintaining the delicate quantum states in the harsh environment of space, must be overcome. Additionally, the high cost of developing and operating quantum sensors presents financial constraints for many research projects.
However, as technology advances and our understanding of quantum mechanics deepens, these challenges are being addressed. The future of quantum sensors in astronomy and astrophysics is bright, with potential breakthroughs on the horizon.
Conclusion
Quantum sensors are pushing the boundaries of what we can observe and comprehend in the vast expanse of the universe. From unraveling the mysteries of dark matter to capturing breathtaking images of distant galaxies, these devices are at the forefront of astronomical and astrophysical research.
As we continue to harness the power of quantum mechanics, we can expect quantum sensors to play an increasingly pivotal role in our quest to understand the cosmos. With each new discovery they enable, we inch closer to a more profound and comprehensive understanding of the universe that has captivated human curiosity for countless generations.