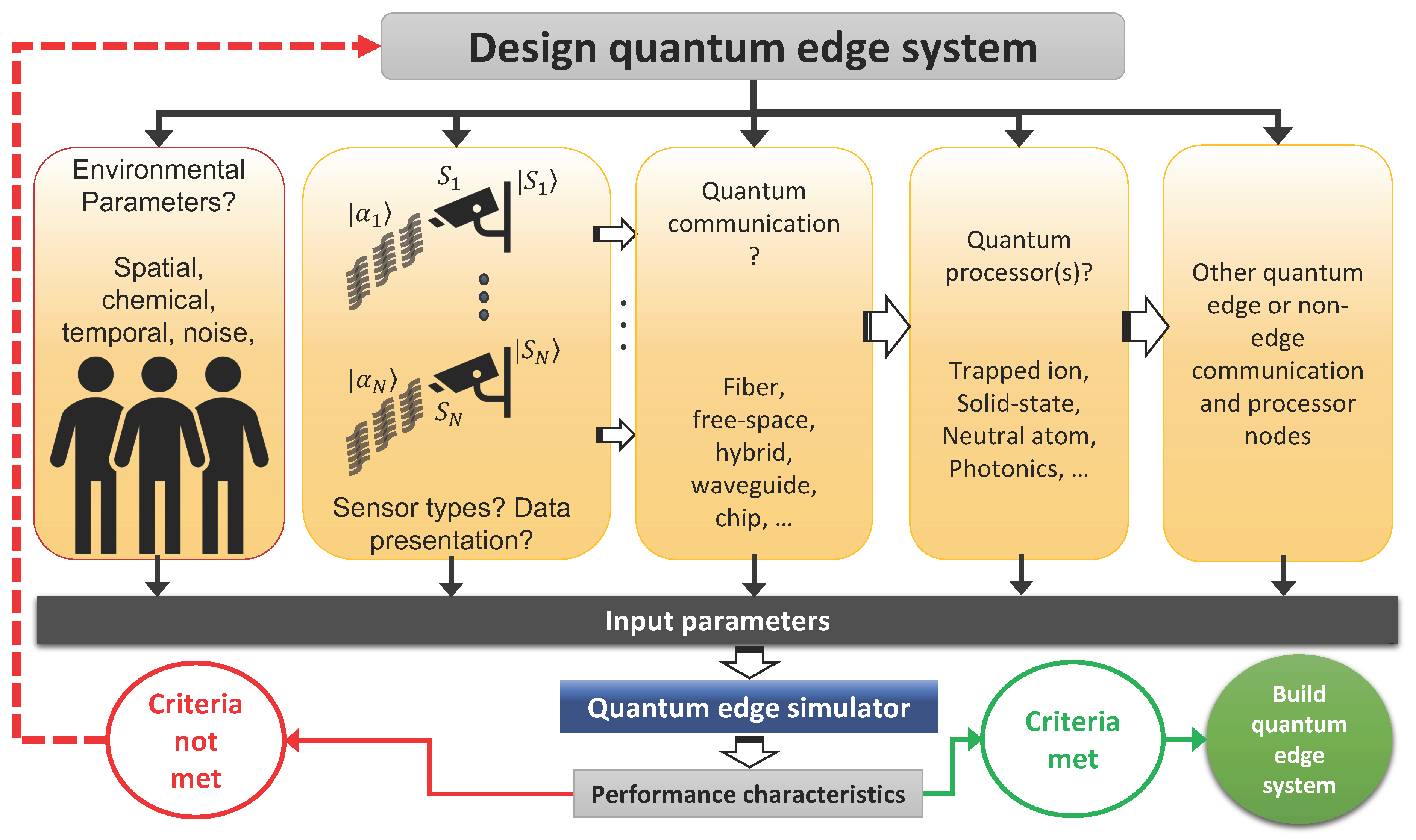
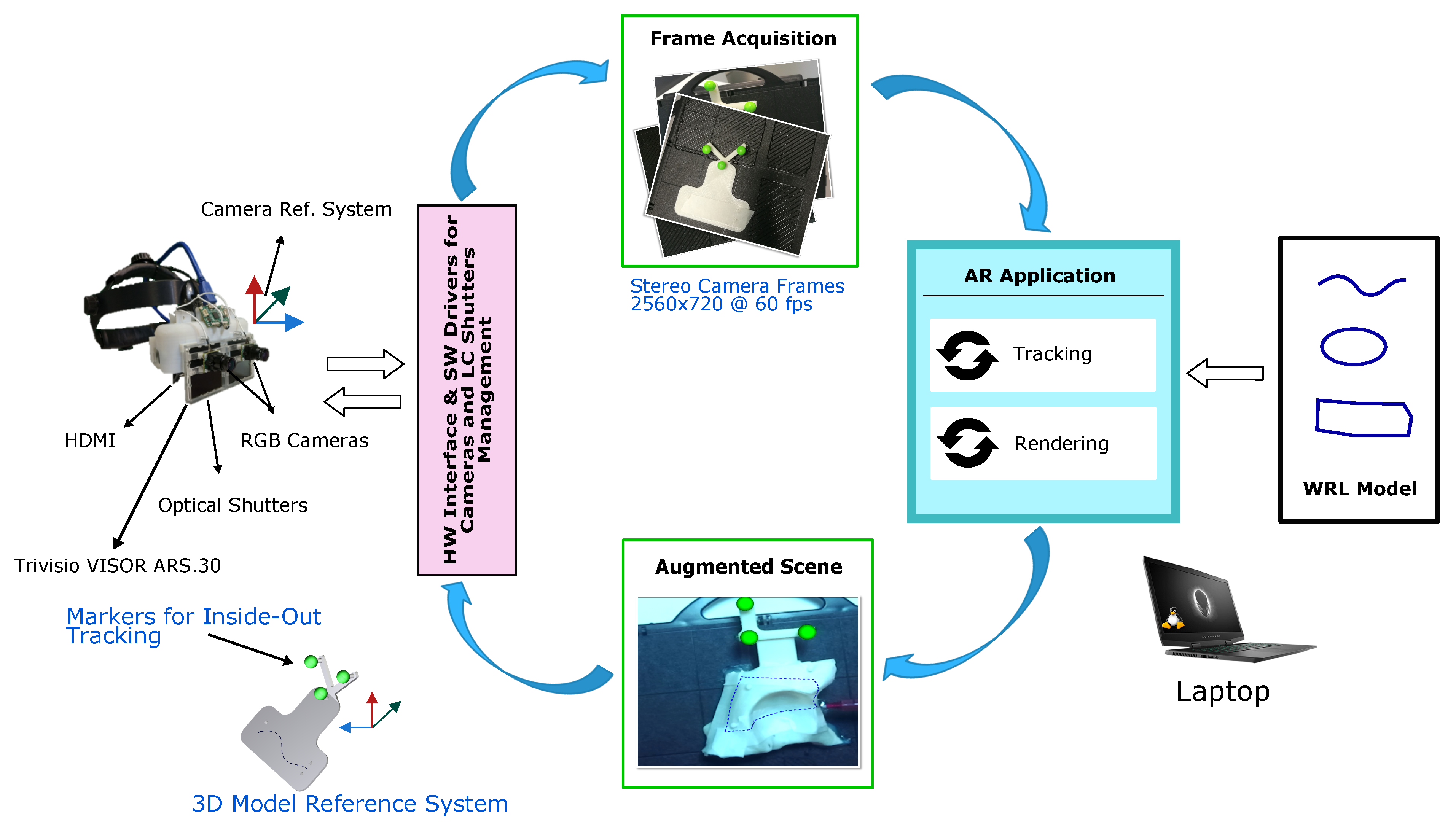
Introduction
Architecture and design have always been fields that push the boundaries of human creativity and innovation. From awe-inspiring skyscrapers to intricately designed interiors, the built environment around us is a testament to human ingenuity. However, as technology continues to advance, architects and designers are exploring new frontiers that are beyond the grasp of traditional tools. One such frontier is quantum sensors, which harness the mind-boggling principles of quantum physics to provide novel solutions for the architectural and design industries.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of quantum sensors, explore their fundamental principles, and examine how they are poised to transform architecture and design as we know it.
Understanding Quantum Sensors
Before we dive into their applications, let’s first gain a basic understanding of what quantum sensors are and how they differ from conventional sensors.
At the heart of quantum sensors lies the strange and counterintuitive world of quantum mechanics. Unlike classical physics, where objects follow predictable paths and states, quantum mechanics deals with the behavior of particles at the smallest scales of the universe. In this quantum realm, particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously, a phenomenon known as superposition, and can become entangled, meaning their properties are interconnected regardless of distance.
Quantum sensors leverage these unique quantum properties to make highly precise measurements. They can measure quantities such as position, time, and electromagnetic fields with unparalleled accuracy. The sensitivity of quantum sensors surpasses that of their classical counterparts, making them invaluable tools in various scientific and industrial applications.
Quantum Sensors in Architecture
Precision Surveying and Geolocation:
One of the primary applications of quantum sensors in architecture is precision surveying and geolocation. Traditional surveying techniques often rely on GPS systems, which have limitations in terms of accuracy, especially in densely built urban areas or when precise measurements are required. Quantum sensors, on the other hand, can offer centimeter-level accuracy in determining positions. This level of precision is vital in architectural projects where even slight errors can lead to significant problems.
Imagine a scenario where architects need to design a new skyscraper in a bustling city. The quantum sensors can precisely measure the distances between buildings, the terrain, and even account for subtle variations in gravitational forces. This information allows architects to optimize the design for structural stability and safety.
Environmental Monitoring:
Quantum sensors also play a pivotal role in environmental monitoring within architectural projects. Whether it’s ensuring proper temperature regulation, monitoring air quality, or assessing the impact of vibrations on a building’s structural integrity, quantum sensors provide real-time data with unmatched accuracy.
For instance, in the design of energy-efficient buildings, quantum sensors can continuously monitor temperature variations throughout the day and adjust heating and cooling systems accordingly. This not only enhances comfort for occupants but also reduces energy consumption, contributing to sustainability goals.
Material Testing and Analysis:
Materials are the building blocks of architecture and design. The choice of materials impacts not only the aesthetics but also the durability and sustainability of a structure. Quantum sensors can be employed to conduct thorough material testing and analysis.
By using quantum sensors to measure properties like material density, thermal conductivity, and elasticity at the quantum level, architects and designers can make informed decisions when selecting materials for their projects. This ensures that the chosen materials are not only aesthetically pleasing but also structurally sound and environmentally friendly.
Quantum Sensors in Design
Lighting Design:
Lighting is a critical element of design, impacting the ambiance, functionality, and aesthetics of a space. Quantum sensors can be used to create dynamic lighting systems that respond in real-time to changes in natural light, occupancy, and user preferences.
For instance, in a smart home, quantum sensors can detect the amount of natural light entering a room and adjust artificial lighting accordingly to maintain the desired illumination levels while conserving energy. This level of adaptability enhances both the comfort and energy efficiency of the space.
Acoustic Design:
Soundscapes play a crucial role in the design of spaces. Quantum sensors can be employed to analyze and optimize acoustic environments. They can measure sound intensity, frequency, and direction, helping designers create spaces with optimal acoustics.
In a concert hall, quantum sensors can adjust the position and intensity of sound-absorbing panels in real-time, ensuring that the audience experiences the best possible audio quality. In open-plan offices, quantum sensors can monitor noise levels and adjust the placement of sound-dampening elements to create a more productive and comfortable workspace.
Biophilic Design:
Biophilic design aims to incorporate natural elements into the built environment to enhance human well-being and connection to nature. Quantum sensors can aid in creating responsive biophilic designs by monitoring factors such as indoor air quality, humidity, and plant health.
Imagine an office with a living green wall. Quantum sensors can detect changes in environmental conditions and trigger irrigation systems to ensure the plants thrive. Additionally, they can monitor air quality and adjust the ventilation system to provide occupants with fresh and clean air, promoting a healthier and more productive work environment.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the potential of quantum sensors in architecture and design is immense, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. Quantum sensors are still in the early stages of development, and their widespread adoption may take time. Additionally, these sensors require highly controlled environments and are sensitive to external factors, which can pose practical challenges in real-world applications.
Nevertheless, ongoing research and technological advancements are expected to overcome these hurdles. As quantum technology matures, we can anticipate a growing integration of quantum sensors into architectural and design processes, leading to more sustainable, efficient, and innovative built environments.
Conclusion
Quantum sensors are poised to revolutionize architecture and design by providing unparalleled precision, responsiveness, and adaptability. From precision surveying and environmental monitoring to lighting design and biophilic integration, these sensors offer a new dimension of possibilities for architects and designers.
As the field of quantum physics continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of quantum sensors. These cutting-edge devices are not just tools; they are the key to unlocking a future where our built environment is not only aesthetically pleasing but also sustainable, efficient, and responsive to the needs of its occupants. The fusion of quantum physics and design is a testament to human creativity, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in architecture and design.