Introduction
In our interconnected world, network security is paramount. With data breaches and cyberattacks becoming increasingly prevalent, safeguarding your network is not just an option; it’s a necessity. One of the most essential components of network security is the firewall. In this blog post, we will take an in-depth look at network security and how firewalls are instrumental in protecting your digital assets.
Understanding Network Security
Network security refers to the practice of safeguarding the usability, integrity, and confidentiality of your network and data. It involves a multitude of strategies, technologies, and practices to protect against unauthorized access, misuse, or any modifications of your network infrastructure and data.
The Importance of Network Security
Network security is vital for several reasons:
Data Protection: In a world where data is a valuable commodity, keeping sensitive information secure is of utmost importance. Network security ensures that your data remains confidential and is not accessible to unauthorized individuals.
Business Continuity: Disruptions to your network can have severe consequences for your organization. Network security measures help ensure that your business operations can continue even in the face of cyberattacks or unforeseen disasters.
Reputation Management: A data breach or security incident can tarnish your company’s reputation. Ensuring network security helps maintain trust among your customers and partners.
Legal Compliance: Many industries have regulations that require data protection and security measures. Complying with these regulations is essential to avoid legal issues and potential fines.
Introducing Firewalls
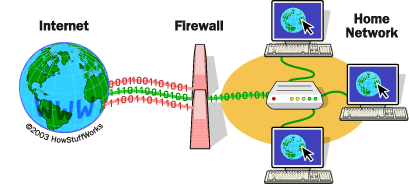
A firewall is a network security device or software that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a barrier between a trusted network (like your organization’s internal network) and an untrusted network (typically the internet). Firewalls use a set of rules to determine whether to allow, block, or filter traffic, thus acting as a gatekeeper for your network.
Types of Firewalls
There are several types of firewalls, each with its unique characteristics and purposes:
Packet Filtering Firewalls: These firewalls examine packets of data as they arrive at the network and determine whether to allow or block them based on predefined rules. They are relatively simple and work at the network layer of the OSI model.
Stateful Inspection Firewalls: Also known as dynamic packet filtering firewalls, these keep track of the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of the traffic. This results in a more secure and intelligent filtering process.
Proxy Firewalls: Proxy firewalls act as intermediaries between a user’s device and the destination server. They inspect the content of the traffic and can provide an extra layer of security by hiding the user’s IP address from potential threats.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): NGFWs combine traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application awareness, and content filtering. They are highly effective at protecting against modern threats.
How Firewalls Work
Firewalls use rules and policies to decide whether to allow or block traffic. These rules can be based on various factors, including the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, protocols, and even the application or service being used. Let’s delve into the key concepts behind how firewalls work:
Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs are a list of rules that dictate how traffic is handled. They specify what is allowed and what is denied based on criteria like IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
Stateful Inspection: Stateful inspection firewalls keep track of the state of active connections. This allows them to make more intelligent decisions based on the context of the traffic. For example, if a request is part of an established connection, it’s more likely to be allowed.
Deep Packet Inspection: Some firewalls can inspect the contents of data packets to identify threats or malicious content. This is particularly useful for detecting and blocking specific applications or protocols that could pose a security risk.
Application Layer Filtering: Next-generation firewalls can analyze traffic at the application layer of the OSI model, making it possible to block specific applications or websites. This level of granularity is crucial for modern network security.
The Role of Firewalls in Network Security
Firewalls play a crucial role in network security in the following ways:
- Traffic Filtering
Firewalls examine incoming and outgoing traffic and apply rules to determine whether it should be allowed or denied. This filtering ensures that potentially harmful or unauthorized traffic is stopped at the perimeter of the network. - Protection Against Threats
Firewalls protect your network from a variety of threats, including malware, viruses, and intrusion attempts. They can detect and block known malicious signatures, making it more difficult for cybercriminals to gain access to your network. - Access Control
By setting up access control rules, firewalls allow you to control who can access your network and what resources they can access. This is crucial for managing user permissions and ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized personnel. - Privacy and Anonymity
Proxy firewalls, in particular, can help protect the privacy and anonymity of users by acting as intermediaries and shielding their IP addresses from potential threats or tracking.
Best Practices for Firewall Configuration
To make the most of your firewall and ensure robust network security, consider these best practices for firewall configuration:
- Regular Updates
Keep your firewall software and firmware up to date. Manufacturers often release updates that address vulnerabilities and improve security. - Strong Authentication
Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication to access your firewall. This prevents unauthorized individuals from making changes to your firewall settings. - Default Deny
Adopt a “default deny” approach, where all traffic is blocked by default, and only specific, necessary traffic is allowed through. This minimizes the attack surface. - Segmentation
Segment your network to limit the spread of an attack. Even if one segment is compromised, it doesn’t mean the entire network is at risk. - Regular Audits
Perform regular audits of your firewall rules and policies. Remove any outdated or unnecessary rules to maintain an efficient and secure network. - Employee Training
Train your employees on security best practices and the importance of adhering to firewall rules. Human error can lead to security breaches, so education is critical. - Redundancy
Consider implementing redundancy in your firewall setup. Having a backup firewall can ensure continuous protection in case of a failure or attack.
Advanced Firewall Features
As network threats continue to evolve, firewalls have also evolved to incorporate advanced features for enhanced security. Here are some of the advanced firewall features that can take your network security to the next level:
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
IPS is a proactive security measure that monitors network and system activities for malicious activities or policy violations. It can block or mitigate threats in real-time, providing an additional layer of defense. - Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Firewalls can often be integrated with VPNs, providing secure and encrypted connections for remote users or branch offices. This ensures that data remains confidential and secure, even when transmitted over untrusted networks. - Application Layer Filtering
Next-generation firewalls excel in application layer filtering, allowing organizations to control and monitor the use of specific applications and websites. This is valuable for productivity and security purposes. - Content Filtering
Content filtering allows you to control the type of content that can be accessed through your network. It can block access to explicit or malicious websites and help ensure a safe browsing environment.
Challenges and Considerations
While firewalls are a fundamental component of network security, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- False Positives
Overly aggressive firewall rules can lead to false positives, where legitimate traffic is mistakenly blocked. Finding the right balance between security and usability is essential. - Encrypted Traffic
With the rise of encrypted communication (e.g., HTTPS), it’s become more challenging to inspect the content of data packets. Firewalls need to adapt to effectively analyze encrypted traffic for threats. - Evolving Threats
Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Firewalls need to stay updated with the latest threat intelligence to effectively protect your network. - User Education
Firewalls alone are not sufficient for network security. Users also need to be educated on best practices and security awareness to minimize the risk of breaches.
Conclusion
Network security is an ever-evolving field, and firewalls remain a cornerstone of defense against cyber threats. By understanding how firewalls work and implementing best practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your network. Whether you’re an individual protecting your home network or an organization safeguarding critical data, the role of firewalls in network security cannot be overstated. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and make network security a top priority in our interconnected digital world.