The history of Telangana, a region in southern India, can be traced back to the ancient period. The region was ruled by various dynasties such as the Satavahanas, the Kakatiyas, and the Qutub Shahis. During the medieval period, Telangana was ruled by the Bahmani Sultanate and later by the Mughals.
In the early 18th century, the region came under the control of the Nizams, who ruled as independent monarchs until the mid-20th century. During British colonial rule, Telangana was part of the Madras Presidency.
After Indian independence in 1947, Telangana became part of the state of Andhra Pradesh, which was created by merging Telangana with the Telugu-speaking regions of Andhra.
However, there were persistent demands for a separate state of Telangana from the 1950s onwards, due to a feeling of neglect and discrimination from the government in Andhra Pradesh. These demands gained momentum in the 2000s, and in 2014, the Indian government announced that Telangana would be carved out as a separate state. Telangana officially became the 29th state of India on June 2, 2014.
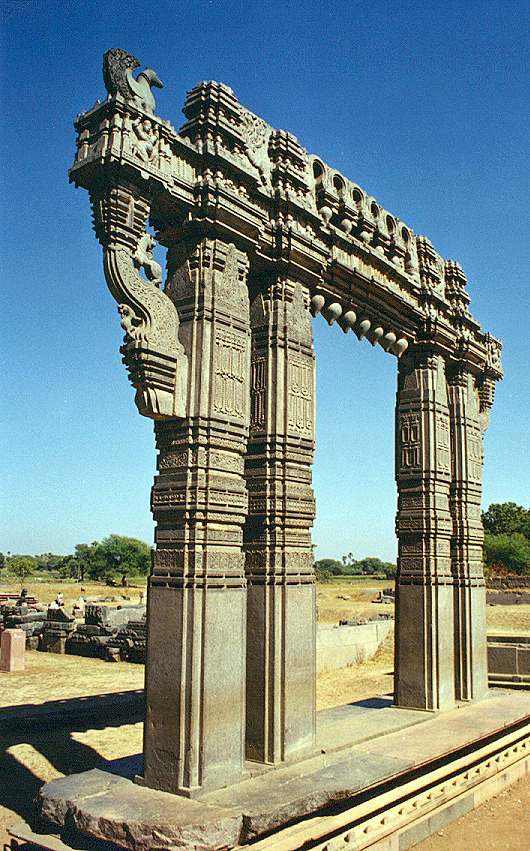
The region is known for its rich cultural heritage, which includes traditional art forms such as Telangana Yakshagana, a theater form, and Telangana Kondapalli toys, a traditional craft. Telangana is also known for its historical sites and monuments, including the Warangal Fort, the Thousand Pillar Temple, and the Qutub Shahi Tombs.
The economy of Telangana is primarily agrarian, with major crops including rice, cotton, and maize. The state is also home to major industries such as pharmaceuticals, IT, and textile.
Overall, Telangana is a state with a rich history, cultural heritage and diverse economy.
Overview:
Telangana is a state located in southern India. It has a rich history dating back to ancient times, when it was ruled by various dynasties such as the Satavahanas, the Kakatiyas, and the Qutub Shahis. During the medieval period, it was ruled by the Bahmani Sultanate and later by the Mughals. In the 18th century, the region came under the control of the Nizams, who ruled as independent monarchs until the mid-20th century. After Indian independence in 1947, Telangana became part of the state of Andhra Pradesh. However, there were persistent demands for a separate state of Telangana from the 1950s onwards, and in 2014, the Indian government announced that Telangana would be carved out as a separate state. The region has a rich cultural heritage, including traditional art forms and historical sites, and an economy primarily based on agriculture and industries such as pharmaceuticals, IT, and textiles.