The Human heart, that powerful organ responsible for pumping life through our veins, can sometimes be a mysterious puzzle. Its rhythms, beats, and electrical impulses are vital indicators of our overall health. Thanks to the advent of modern medical technology, we can now unravel the secrets of the heart with precision and ease. One such technological marvel is the Electrocardiogram (ECG) machine, a device that has become an indispensable tool for cardiologists and healthcare professionals worldwide.
In this extensive exploration, we will take you on a journey through the world of ECG machines. We will uncover their history, mechanisms, applications, and the latest innovations that continue to shape the field of cardiology.
The Evolution of ECG Machines
To truly understand the significance of ECG machines, we must first delve into their history. The roots of electrocardiography can be traced back to the late 19th century when scientists and physicians were just beginning to unravel the mysteries of the human heart.
One of the key figures in the development of ECG technology was Willem Einthoven, a Dutch physiologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1924 for his groundbreaking work on the electrocardiogram. Einthoven’s invention, the string galvanometer, marked the birth of modern ECG machines. It allowed for the accurate recording of electrical signals generated by the heart, paving the way for more precise diagnosis and treatment of cardiac conditions.
Over the years, ECG machines have evolved significantly. They have become more compact, portable, and user-friendly, making them accessible to a broader range of healthcare professionals. Modern ECG machines are equipped with advanced features, such as wireless connectivity, real-time monitoring, and digital data storage, enabling quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
How ECG Machines Work
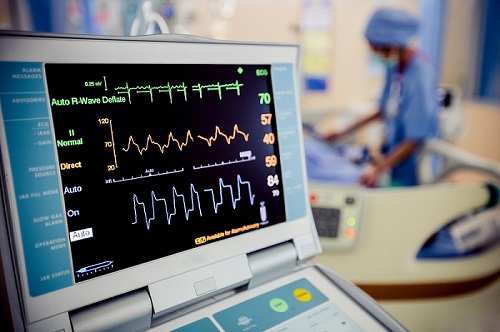
To grasp the significance of ECG machines, it’s essential to understand how they work. At their core, ECG machines capture the electrical activity of the heart. This activity is represented graphically as an electrocardiogram, a visual representation of the heart’s electrical impulses.
The ECG procedure is non-invasive and involves attaching electrodes to specific points on the patient’s body. These electrodes are strategically placed on the chest, limbs, and sometimes the legs. As the heart beats, it generates electrical impulses that travel through the body. The ECG machine detects these impulses and records them as waves on a graph. Each wave corresponds to a specific phase of the heart’s activity, providing valuable information about its health.
Applications of ECG Machines
ECG machines have a broad range of applications in the field of cardiology and beyond. These applications extend to both clinical settings and research. Some of the primary uses of ECG machines include:
Diagnosis of Heart Conditions: ECGs are instrumental in diagnosing various heart conditions, such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction (heart attacks), and heart valve disorders. The distinctive patterns on the ECG can reveal abnormalities in heart rhythms and function.
Risk Assessment: ECGs are used to assess an individual’s risk of heart disease. They can identify early signs of heart problems and help healthcare professionals develop preventive strategies.
Monitoring and Treatment: ECG machines are crucial for continuous monitoring of patients with known heart conditions. They help doctors adjust treatment plans and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
Research and Clinical Trials: ECG data plays a vital role in research, allowing scientists to better understand heart diseases and develop new treatments. ECGs are also used in clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new medications and medical devices.
Advancements in ECG Technology
The field of ECG technology is continually advancing, with innovations that promise to enhance the accuracy and convenience of cardiac monitoring. Here are some of the notable advancements in ECG technology:
Wearable ECG Devices: The rise of wearable technology has brought about the development of wearable ECG devices that individuals can use to monitor their heart health in real time. These devices provide continuous data, empowering users to take control of their heart health.
Telemedicine Integration: ECG machines are increasingly integrated into telemedicine platforms, allowing patients to transmit their ECG data to healthcare providers remotely. This has been especially valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic, enabling safe and efficient monitoring of patients from a distance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are being employed to analyze ECG data rapidly and accurately. AI can detect subtle abnormalities that may go unnoticed by human observers, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Smartphone Connectivity: ECG machines can now be connected to smartphones, making it easier for patients to record and share their ECG data with their healthcare providers. This seamless integration enhances the accessibility of ECG technology.
Conclusion
Electrocardiogram (ECG) machines have undoubtedly revolutionized the field of cardiology and healthcare at large. They provide invaluable insights into the heart’s electrical activity, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of various cardiac conditions. The rich history, mechanisms, and applications of ECG machines showcase their enduring significance in modern medicine.
As technology continues to advance, ECG machines are becoming more accessible, user-friendly, and integrated into our daily lives. The latest innovations in ECG technology promise to make heart health monitoring even more convenient and accurate, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
In a world where heart disease remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, ECG machines stand as a beacon of hope, offering both healthcare professionals and individuals the tools they need to protect and preserve the most vital organ in the human body – the heart.