Introduction
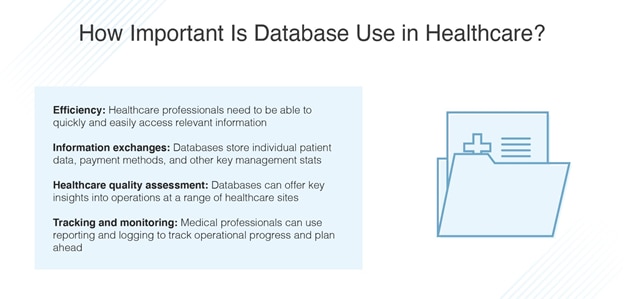
Healthcare systems generate and store vast amounts of data daily. From electronic health records (EHRs) to patient demographics, treatment histories, medical images, and billing information, healthcare databases are repositories of invaluable information. Efficiently managing this data is not just a matter of organization; it directly impacts patient care, regulatory compliance, and the overall functioning of healthcare institutions.
In this blog post, we explore the world of database administration in the context of healthcare systems, shedding light on its importance, challenges, best practices, and the profound effect it has on patient outcomes and healthcare organizations.
The Significance of Database Administration in Healthcare
Data Security and Privacy: Healthcare databases contain sensitive patient information that must be protected at all costs. Database administrators (DBAs) play a pivotal role in implementing robust security measures to safeguard this data against breaches and unauthorized access.
Data Integrity: Inaccurate or incomplete patient data can lead to medical errors with potentially dire consequences. DBAs ensure data integrity by implementing validation checks and maintaining data quality.
Availability and Reliability: Healthcare operates around the clock, and any downtime or data unavailability can hinder patient care. DBAs employ high-availability solutions, redundancy, and disaster recovery plans to ensure that data is always accessible.
Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare is heavily regulated, with laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) imposing strict data handling requirements. DBAs must ensure that databases adhere to these regulations to avoid costly penalties and legal issues.
Challenges in Healthcare Database Administration
While the significance of database administration in healthcare is undeniable, it comes with its own set of challenges:
Data Volume: Healthcare databases can be massive, making data storage and retrieval a complex task. DBAs need to optimize database performance to handle large datasets efficiently.
Interoperability: Healthcare systems often use a variety of software and platforms, leading to interoperability issues. DBAs must work to ensure that data can seamlessly flow between different systems.
Scalability: As healthcare organizations grow, so does the volume of data. DBAs must plan for scalability to accommodate future data growth without compromising performance.
Emerging Technologies: The healthcare industry continually adopts new technologies like telemedicine and wearable devices. DBAs need to adapt databases to integrate these technologies smoothly.
Best Practices in Healthcare Database Administration
To overcome the challenges and fulfill the critical role in healthcare, DBAs should follow these best practices:
Regular Backup and Recovery: Implement robust backup and recovery strategies to safeguard against data loss due to system failures or cyberattacks.
Performance Optimization: Continuously monitor and optimize database performance to ensure fast and reliable data access.
Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive patient data both in transit and at rest to enhance security.
Compliance Audits: Conduct regular compliance audits to ensure that the database aligns with healthcare regulations.
Training and Education: Keep the DBA team updated with the latest healthcare technology trends and best practices.
Impact on Patient Care
Efficient database administration directly influences patient care in several ways:
Faster Access to Information: Quick access to patient data allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions promptly, leading to better patient outcomes.
Reduced Errors: Data validation and integrity measures minimize the risk of errors in diagnoses and treatment.
Improved Coordination: Interoperable databases facilitate seamless communication between different healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care.
Enhanced Research: Healthcare databases also play a crucial role in medical research, enabling scientists and researchers to access a wealth of anonymized patient data for studies and discoveries.
Impact on Healthcare Organizations
Beyond patient care, efficient database administration has a substantial impact on healthcare organizations:
Cost Savings: Optimized databases reduce operational costs, including hardware maintenance and energy consumption.
Reputation Management: Strong data security and privacy practices enhance an organization’s reputation, fostering trust among patients and partners.
Data-Driven Decisions: Access to accurate, timely data allows healthcare organizations to make informed decisions about resource allocation, strategic planning, and process improvement.
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to healthcare regulations avoids costly fines and legal troubles, ensuring the organization’s financial stability.
Conclusion
Database administration is the unsung hero behind the scenes of healthcare systems, ensuring that critical data flows seamlessly, securely, and reliably. From safeguarding patient privacy to enabling data-driven decisions and enhancing patient care, DBAs play a pivotal role in the success of healthcare organizations.
In an era where data is king, healthcare database administrators are the guardians of the kingdom, and their expertise is indispensable. As technology continues to advance and healthcare evolves, the importance of effective database administration will only grow, making it a vital component of the healthcare ecosystem. By recognizing its significance and investing in best practices, healthcare organizations can harness the full potential of their data to improve patient care and drive operational excellence.