Introduction
Wearable devices, once a niche market, have exploded in popularity over the past decade. From fitness trackers and smartwatches to augmented reality glasses, these gadgets have seamlessly integrated into our daily routines, offering convenience, entertainment, and valuable health insights. However, with the growing ubiquity of wearable technology comes a pressing concern: the security of our personal data.
In this digital age, data is a currency. From our health metrics and location data to payment information and biometric details, wearables collect an astonishing array of information about us. This treasure trove of data, if not adequately protected, can become a goldmine for cybercriminals. To address these concerns, let’s delve into the world of cybersecurity and wearable devices, exploring the risks and solutions to ensure your personal data remains secure.
The Proliferation of Wearable Devices
Wearable devices have witnessed a rapid evolution. Initially, they were primarily fitness-focused, designed to track steps, heart rate, and sleep patterns. Today, wearables have diversified into various categories, including:
Smartwatches: These devices not only tell time but also offer smartphone-like functionality. They can handle calls, send messages, and run applications.
Fitness Trackers: Still popular, fitness trackers have evolved to measure a wide range of health metrics, from blood oxygen levels to stress levels.
Augmented Reality (AR) Glasses: AR glasses overlay digital information onto the real world, offering exciting possibilities for gaming, navigation, and more.
Hearables: These smart earbuds do more than just play music; they offer features like voice assistants and fitness tracking.
Smart Clothing: Embedded sensors in clothing can monitor posture, track movements, and even provide haptic feedback.
This proliferation of wearable devices underscores the need to address the security aspects associated with them.
Cybersecurity Risks with Wearables
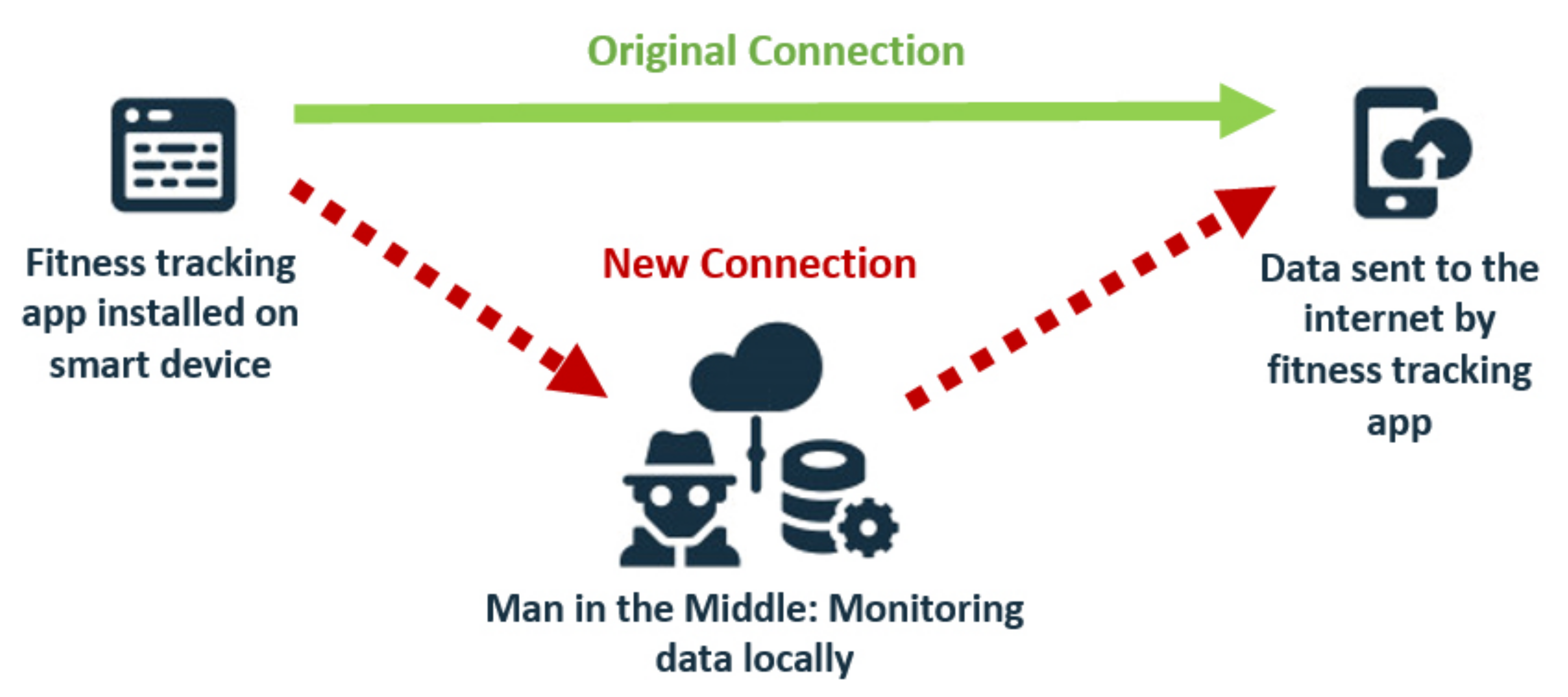
Data Breaches: Wearables collect an extensive amount of personal data, including biometrics, health information, and location data. If not adequately protected, this information can be compromised in a data breach, leading to identity theft or other malicious activities.
Privacy Concerns: The constant monitoring of individuals’ activities and health data raises significant privacy concerns. Unauthorized access to this information can result in a breach of an individual’s privacy rights.
Health Data Vulnerabilities: The health data collected by wearables is particularly sensitive. If this data falls into the wrong hands, it can be used for insurance fraud, blackmail, or other harmful purposes.
Device Vulnerabilities: Like any connected device, wearables can be vulnerable to malware and hacking attempts. Attackers could compromise the device itself, leading to data theft or unauthorized access.
Eavesdropping: Certain wearable devices, such as hearables and AR glasses, have microphones and cameras. These can be exploited for eavesdropping or recording without the user’s consent.
Securing Your Wearable Devices
Now that we understand the potential risks, let’s explore how you can secure your wearable devices and the personal data they collect.
Strong Passwords and Biometrics: Ensure your wearable device is protected by a strong password or PIN. Many devices also offer biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, which adds an extra layer of security.
Regular Software Updates: Keep your wearable’s firmware and software up to date. Manufacturers often release updates that include security patches to address vulnerabilities.
Data Encryption: Enable data encryption on your device to protect the information it stores or transmits. This ensures that even if someone gains access to your device, they won’t be able to decipher your data.
App Permissions: Be cautious about the permissions you grant to apps that interact with your wearable. Only provide access to the data and features necessary for the app’s functionality.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If your wearable device supports 2FA, enable it. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a secondary authentication method, such as a text message code or authentication app.
Use Secure Networks: When syncing or transmitting data from your wearable to your smartphone or the cloud, use secure, trusted networks. Avoid public Wi-Fi networks, which can be less secure.
Review Privacy Settings: Regularly review and update the privacy settings on your wearable device and its associated apps. You can often customize what data is shared and with whom.
Physical Security: Be mindful of the physical security of your wearable. Don’t leave it unattended in public places, and consider using a lock screen or PIN to prevent unauthorized access.
Install Antivirus Software: If your wearable device allows it, consider installing antivirus or security software to protect against malware and other threats.
Monitor for Suspicious Activity: Keep an eye on your wearable device for any unusual or unexpected behavior. This can include unexpected battery drain, unauthorized data access, or strange app behavior.
Conclusion
Wearable devices have undoubtedly enhanced our lives in numerous ways, but they also come with cybersecurity risks that should not be underestimated. As these devices continue to evolve and collect increasingly sensitive data, it becomes imperative for both manufacturers and users to prioritize cybersecurity.
By following the security tips outlined in this blog post, you can help ensure that your personal data remains secure while enjoying the benefits of wearable technology. As the world becomes more connected through the Internet of Things (IoT), taking proactive steps to protect your data has never been more important. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay secure. Your digital well-being depends on it.