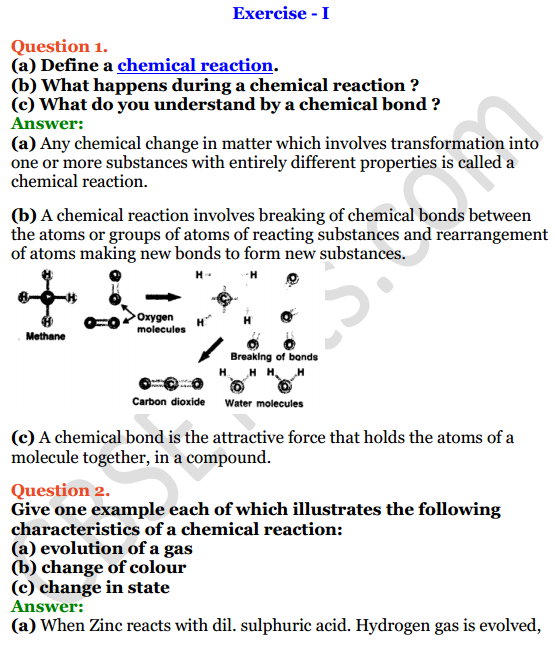
Chemical reactions are processes that involve the transformation of one or more substances into new substances with different properties. Chemical reactions can involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, which leads to the rearrangement of atoms and molecules.
Chemical reactions can be classified into several categories based on the type of reaction that occurs. These categories include combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, redox reactions, acid-base reactions, and precipitation reactions.
Combination reactions occur when two or more substances combine to form a single new substance. For example, the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water is a combination reaction.
Decomposition reactions occur when a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances. For example, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen is a decomposition reaction.
Displacement reactions occur when an element or a group of elements is displaced from one compound and replaced by another element or group of elements. For example, the reaction between iron and copper sulfate to form iron sulfate and copper is a displacement reaction.
Redox reactions, also known as oxidation-reduction reactions, involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another. In these reactions, one species loses electrons (is oxidized) while another species gains electrons (is reduced).
Acid-base reactions occur when an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. These reactions are important in many industrial and biological processes, including the production of fertilizers and the digestion of food.
Precipitation reactions occur when two solutions are mixed and a solid precipitate is formed. These reactions are important in the purification of water and the synthesis of new materials.
Factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions include temperature, concentration, surface area, and catalysts. Increasing the temperature, concentration, or surface area of the reactants typically leads to an increase in the rate of the reaction. Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of the reaction without being consumed in the process.
Chemical reactions are important in everyday life. They are involved in processes such as digestion, respiration, and photosynthesis. Chemical reactions are also important in the production of many common products, such as fertilizers, plastics, and medicines.
In conclusion, chemical reactions are an essential aspect of chemistry and play a vital role in many processes and applications. Understanding the basics of chemical reactions, including the types of reactions and the factors that affect their rates, can provide insight into the behavior of matter and the world around us.