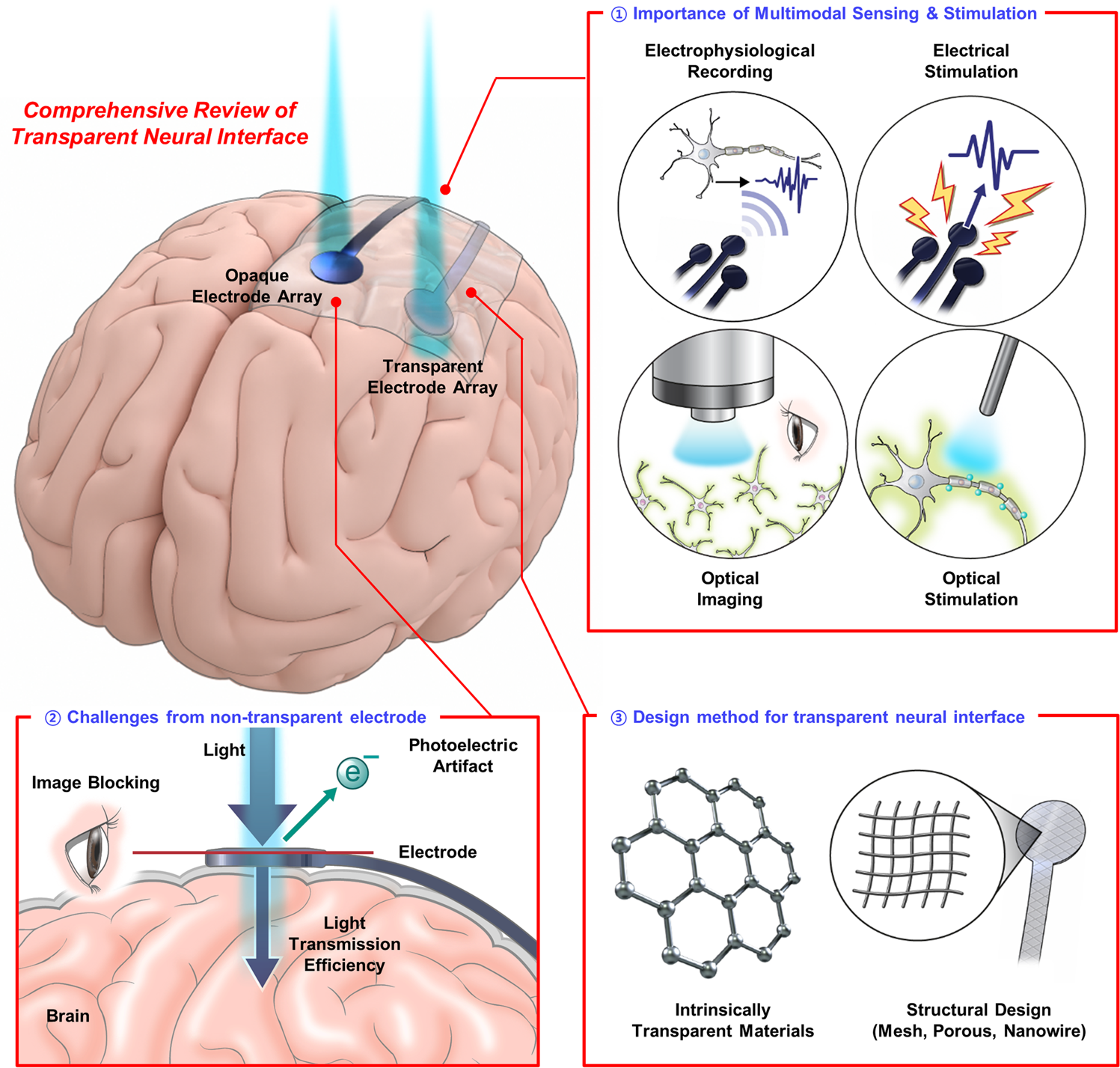
The Promise of Brain Implants
Brain implants, also known as neural implants or brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), are a class of neurotechnology devices that are surgically implanted into the brain. These devices can record neural activity, stimulate specific brain regions, or even enable direct communication between the brain and external devices. The potential applications of brain implants are vast, ranging from restoring lost sensory functions to treating neurological disorders and augmenting human cognition.
One of the most promising aspects of brain implants is their ability to provide real-time insights into brain activity. Researchers and medical professionals can use this data to better understand how the brain functions under various conditions and to develop more targeted therapies for neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and depression. However, to fully harness the potential of brain implants, we need robust tools for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing the vast amounts of data they generate.
The Data Deluge from Brain Implants
Imagine a tiny device implanted in your brain, continuously recording electrical signals from thousands of neurons. This data stream contains a wealth of information about your brain’s activity, from the firing patterns of individual neurons to complex neural network dynamics. To make sense of this data and translate it into actionable insights, we require advanced analytical tools, and this is where Business Intelligence comes into play.
Business Intelligence, often abbreviated as BI, is a set of technologies and processes that transform raw data into meaningful information for decision-making. Traditionally, BI has been used in corporate settings for tasks like sales forecasting, financial analysis, and customer segmentation. However, its application is expanding beyond the business world into diverse fields, including healthcare and neuroscience.
Leveraging Business Intelligence for Brain Implants
- Real-time Data Processing
One of the key advantages of BI in the context of brain implants is its ability to process data in real-time. The continuous stream of neural data generated by brain implants can be overwhelming to analyze manually. BI tools can automate the process of data collection, cleansing, and analysis, providing researchers and clinicians with immediate insights into a patient’s brain activity. - Predictive Analytics
BI tools excel in predictive analytics, which involves using historical data to make predictions about future events. In the case of brain implants, predictive analytics can help identify early warning signs of neurological disorders or anticipate changes in brain activity patterns. This proactive approach to healthcare can lead to more effective treatments and improved patient outcomes. - Data Visualization
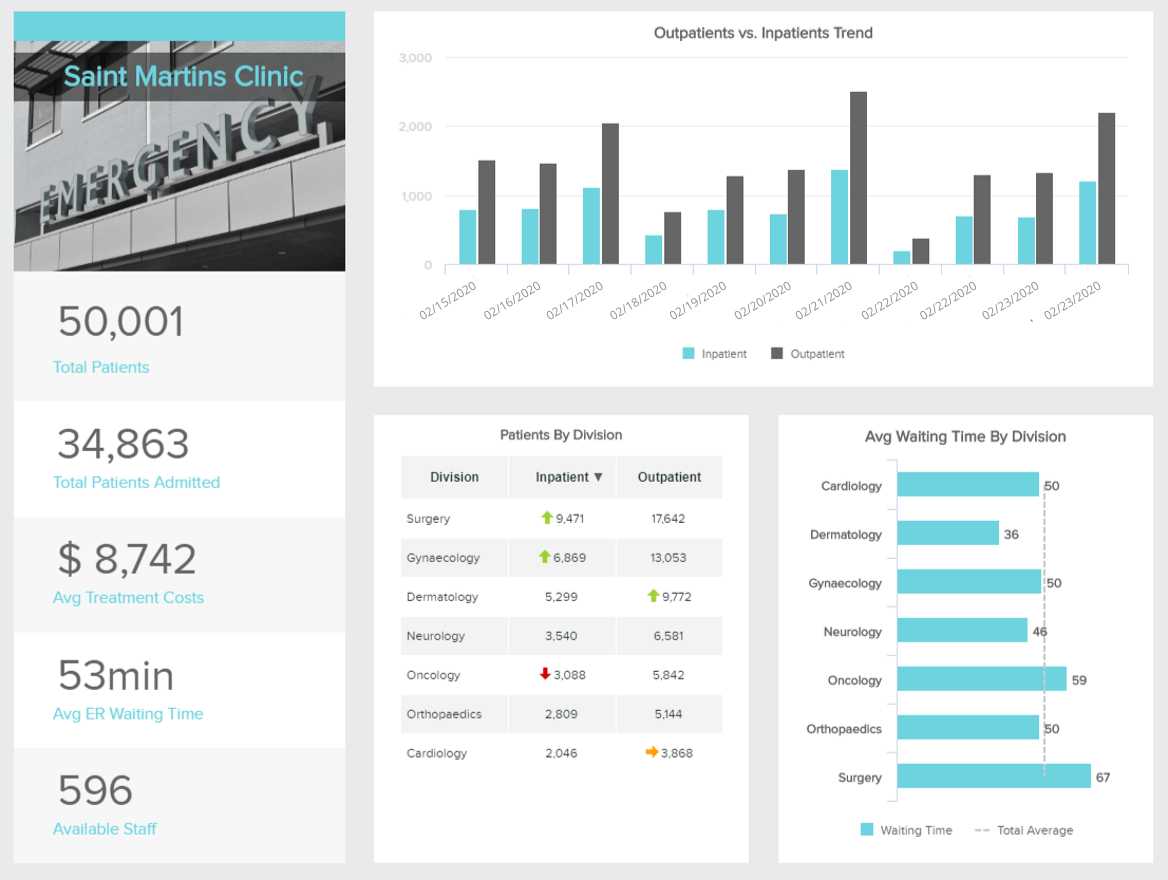
Effective communication of data is crucial in healthcare. BI tools offer advanced data visualization capabilities, allowing healthcare professionals to create interactive graphs, charts, and dashboards that make complex neural data more accessible and understandable. This not only aids in diagnosis but also enhances patient engagement and understanding. - Longitudinal Studies
Brain implant data is most valuable when analyzed over extended periods. BI tools can facilitate longitudinal studies by securely storing and tracking changes in brain activity over time. This longitudinal approach is vital for gaining deeper insights into how the brain adapts and evolves, both in healthy individuals and those with neurological conditions.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the integration of BI with brain implants holds immense promise, it also raises significant challenges and ethical questions. Here are a few important considerations:
- Data Privacy and Security
The data generated by brain implants is highly sensitive and personal. Ensuring robust data privacy and security measures is paramount to protect individuals from unauthorized access to their neural data. - Informed Consent
Implanting a device into the brain is a major medical procedure. Obtaining informed consent from patients, including a clear understanding of how their neural data will be used, is crucial. - Bias and Fairness
BI algorithms are not immune to bias, and this can have serious consequences when applied to healthcare data. Ensuring that BI tools are fair and unbiased is essential to provide equitable care to all patients. - Regulatory Oversight
The use of BI in healthcare, especially in conjunction with brain implants, requires robust regulatory oversight to ensure safety and efficacy. Regulatory bodies must adapt to the evolving landscape of neurotechnology.
Conclusion
The convergence of brain implants and Business Intelligence presents an exciting frontier in healthcare and neuroscience. It has the potential to transform our understanding of the brain and improve the lives of individuals with neurological conditions. However, it also comes with significant responsibilities and challenges related to data privacy, ethics, and regulation. As we navigate this uncharted territory, it’s essential to strike a balance between innovation and ethics to unlock the full potential of this groundbreaking technology. The future of brain implant monitoring is here, and it holds the promise of a healthier, more informed, and interconnected world.