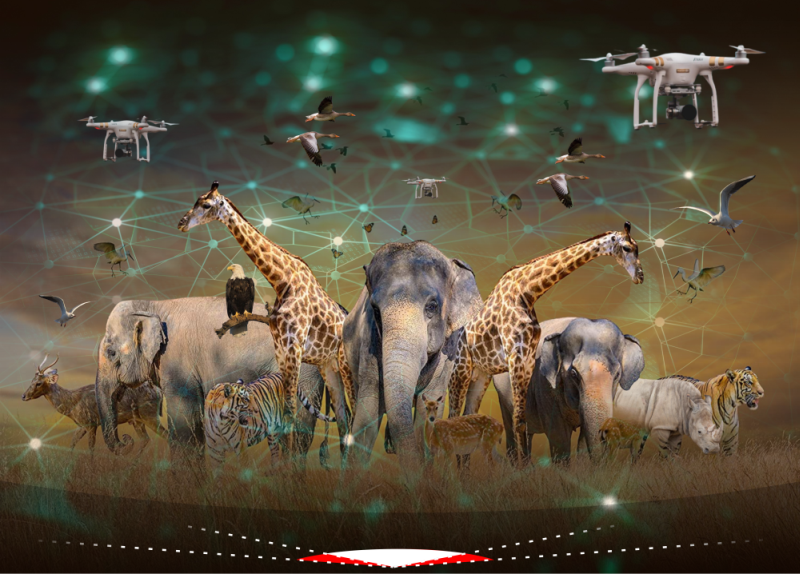
Introduction
Our planet is home to an astonishing array of wildlife, from the majestic elephants roaming the savannas of Africa to the tiny sea turtles making their way to the ocean. However, these magnificent creatures face numerous threats, including habitat loss, climate change, and illegal wildlife trade. The need for innovative approaches to conservation has never been more urgent, and one of the most promising tools in our arsenal is artificial intelligence (AI).
AI is not just a buzzword in tech circles; it’s a game-changer in wildlife conservation. It offers the potential to revolutionize how we monitor, protect, and ultimately save endangered species and fragile ecosystems. In this blog post, we’ll explore the profound impact of AI on wildlife conservation and the incredible ways it is being used to protect biodiversity.
AI-Powered Surveillance
One of the primary challenges in wildlife conservation is monitoring and tracking animals in their natural habitats. Traditional methods, such as radio collars and camera traps, have limitations in terms of coverage and efficiency. AI changes the game by enabling real-time, remote monitoring of wildlife populations.
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from cameras and acoustic sensors, identifying species, tracking their movements, and even predicting behaviors. For example, the Wildbook project uses AI to identify individual animals based on their unique markings, like the stripes of a zebra or the spots of a cheetah. This helps researchers track population trends and migration patterns more accurately.
Furthermore, drones equipped with AI technology are being used to survey large and remote areas, providing a bird’s-eye view of the environment. Conservationists can use this data to detect illegal activities like poaching or deforestation, allowing for rapid intervention.
AI in Predictive Analysis
Conservationists are increasingly using AI-driven predictive analytics to anticipate and mitigate threats to wildlife. Machine learning algorithms can process historical data on environmental conditions, animal behavior, and human activities to make predictions about future trends.
For instance, scientists are using AI to forecast the impact of climate change on species distribution. By analyzing temperature, precipitation, and habitat data, AI models can predict how habitats will shift and help conservationists plan for potential relocations of endangered species.
Additionally, AI-powered predictive models are instrumental in combating poaching. By analyzing historical poaching data, machine learning algorithms can identify high-risk areas and times when illegal hunting is most likely to occur. This allows law enforcement and conservation agencies to allocate their resources more effectively, resulting in increased protection for endangered animals.
AI-Assisted Wildlife Health Monitoring
Understanding the health of wildlife populations is crucial for effective conservation. AI is playing a vital role in non-invasive health monitoring, helping researchers assess the well-being of animals without causing unnecessary stress or harm.
One innovative application of AI is in bioacoustics. By analyzing the sounds made by animals, such as bird calls or whale songs, AI algorithms can detect signs of distress, illness, or changes in behavior. This technology can be especially useful for monitoring elusive or nocturnal species that are difficult to observe directly.
In addition to acoustics, AI is being used to analyze images of wildlife to detect signs of disease or injury. For example, researchers are using AI to analyze drone images of coral reefs to identify areas affected by coral bleaching, a sign of stress in these vital ecosystems.
AI-Powered Conservation Decisions
Effective conservation requires making informed decisions based on data-driven insights. AI helps conservationists sift through vast amounts of data to make informed choices about resource allocation, policy development, and conservation strategies.
Machine learning models can analyze complex ecological interactions and recommend interventions that are most likely to succeed. Whether it’s restoring a degraded habitat, implementing a captive breeding program, or changing hunting regulations, AI can provide valuable guidance to decision-makers.
Furthermore, AI can assist in optimizing patrol routes for wildlife rangers, ensuring that limited resources are deployed where they are needed most. This not only increases the efficiency of conservation efforts but also improves the safety of rangers working in remote and often dangerous environments.
Conclusion
The integration of artificial intelligence into wildlife conservation represents a remarkable leap forward in our ability to protect the planet’s biodiversity. AI-powered surveillance, predictive analysis, wildlife health monitoring, and decision-making tools are revolutionizing the way we approach conservation efforts.
As the threats to wildlife and ecosystems continue to evolve, so too must our conservation strategies. AI provides a dynamic and adaptable solution to the challenges we face in safeguarding the natural world. By harnessing the power of technology, we can hope to preserve the beauty and diversity of our planet’s wildlife for generations to come.
In the ongoing battle to protect endangered species and conserve fragile ecosystems, AI isn’t just a tool; it’s a lifeline. It’s the digital guardian of our natural world, helping us ensure that the songs of birds, the roar of lions, and the grace of dolphins continue to echo through our planet’s wild places. Together with AI, we can forge a brighter future for wildlife and a healthier planet for all.