The human respiratory system is an intricate network of organs and tissues designed to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. When this system encounters issues, it can lead to life-threatening situations, necessitating the use of ventilators and various respiratory support devices to provide essential assistance. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of respiratory and ventilatory devices, understanding their importance, types, and how they function.
Understanding the Need for Respiratory Support
Breathing is a fundamental aspect of life. Our respiratory system allows us to take in the oxygen our cells need and expel the waste product, carbon dioxide. However, various health conditions and emergencies can disrupt this process. These disruptions may include:
Respiratory Infections: Conditions like pneumonia, bronchitis, or severe flu can impair lung function, making it difficult for individuals to breathe adequately.
Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma can cause long-term respiratory issues, making it challenging for patients to maintain normal breathing patterns.
Trauma and Surgery: In cases of severe injury or surgery, patients may need temporary assistance with their breathing to aid recovery.
Critical Illness: Conditions like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or sepsis can critically affect lung function and require intensive care support.
Neuromuscular Disorders: Certain neurological conditions weaken the muscles involved in breathing, necessitating external support.
The Role of Ventilators
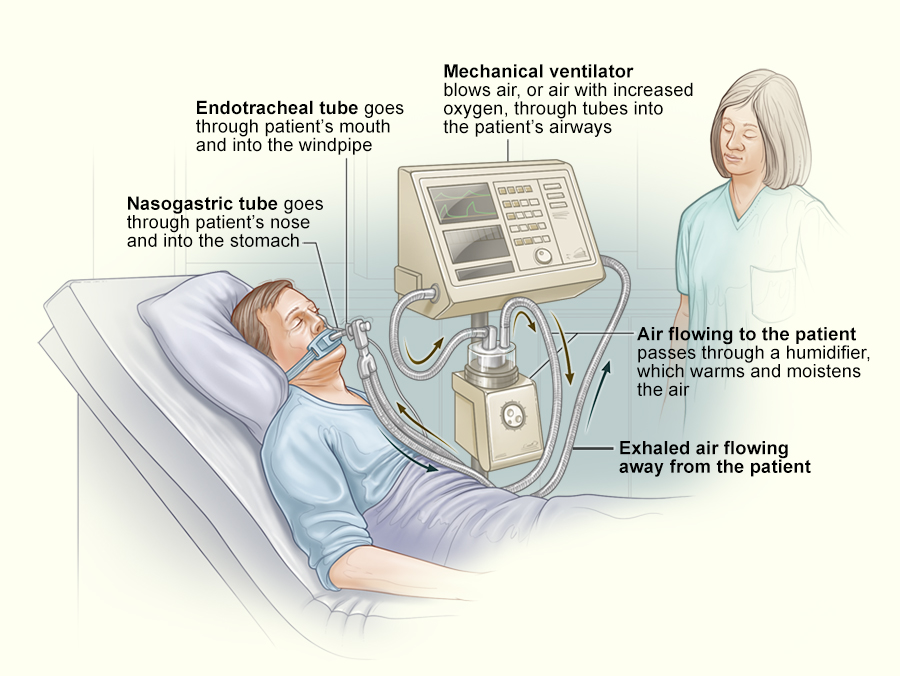
Ventilators, also known as mechanical ventilators or respirators, are life-saving medical devices that assist individuals with compromised respiratory function. These machines deliver a controlled mixture of oxygen and air to the patient’s lungs and remove carbon dioxide. Here’s how they work:
Inhalation: The ventilator pushes a mixture of oxygen and air into the patient’s lungs through an endotracheal tube or a mask.
Exhalation: It allows passive exhalation by letting the patient’s natural exhalation process occur, or in some cases, it assists in actively pushing out air.
Ventilators come in various forms, including invasive and non-invasive options. Invasive ventilation involves the insertion of a tube into the patient’s airway, while non-invasive ventilation utilizes masks or nasal prongs. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of respiratory distress.
Non-Invasive Respiratory Support
In less severe cases of respiratory distress, non-invasive respiratory support devices can be highly effective. These devices do not require the insertion of a tube into the patient’s airway and are often more comfortable for the individual. They include:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP machines deliver a continuous flow of air at a fixed pressure to help keep the airways open. This is particularly useful for patients with sleep apnea.
Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP): BiPAP machines provide varying levels of pressure for inhalation and exhalation. They are commonly used in cases of respiratory failure.
Nasal Cannula: A nasal cannula is a simple device that delivers oxygen through small tubes placed in the nostrils. It is often used for individuals requiring low to moderate oxygen supplementation.
The Importance of Respiratory Health
Respiratory health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being. When our respiratory system functions optimally, our bodies receive the oxygen they need to perform essential functions. However, when this system fails, it can lead to complications and potentially life-threatening situations.
Proper care for respiratory health involves a range of measures, from avoiding smoking and environmental toxins to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and staying hydrated all contribute to better lung health.
The Future of Respiratory and Ventilatory Devices
The field of respiratory and ventilatory devices is continuously evolving. Technological advancements have led to the development of more efficient and user-friendly devices. Here are some trends that we can expect to see in the future:
Miniaturization: Devices are becoming smaller and more portable, allowing for easier home use.
Telemedicine Integration: Remote monitoring and telemedicine are being integrated into respiratory support devices, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients more effectively.
Data Analytics: Data collected from these devices can be used to tailor treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
Improved Patient Comfort: Efforts are ongoing to make these devices more comfortable and less intrusive for patients.
Conclusion
In times of respiratory distress, ventilators and other respiratory support devices play a critical role in saving lives. They provide the assistance needed to ensure that individuals with compromised respiratory function can continue to breathe and recover. With ongoing advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of respiratory health, the future holds promise for more effective and patient-friendly devices.
Respiratory health is an integral part of overall well-being. To maintain good respiratory health, it’s essential to adopt a healthy lifestyle and seek medical attention when needed. Whether it’s a non-invasive device like a CPAP machine or a life-saving ventilator, these devices are essential in the world of healthcare, ensuring that every breath counts.