Unraveling the Mysteries of the Brain with EEG
The human brain is often described as the most complex structure in the known universe. It’s a vast network of billions of neurons, constantly communicating through electrical impulses. These intricate electrical patterns are the foundation of our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. To study and monitor these patterns, we turn to Electroencephalography, or EEG.
What is EEG?
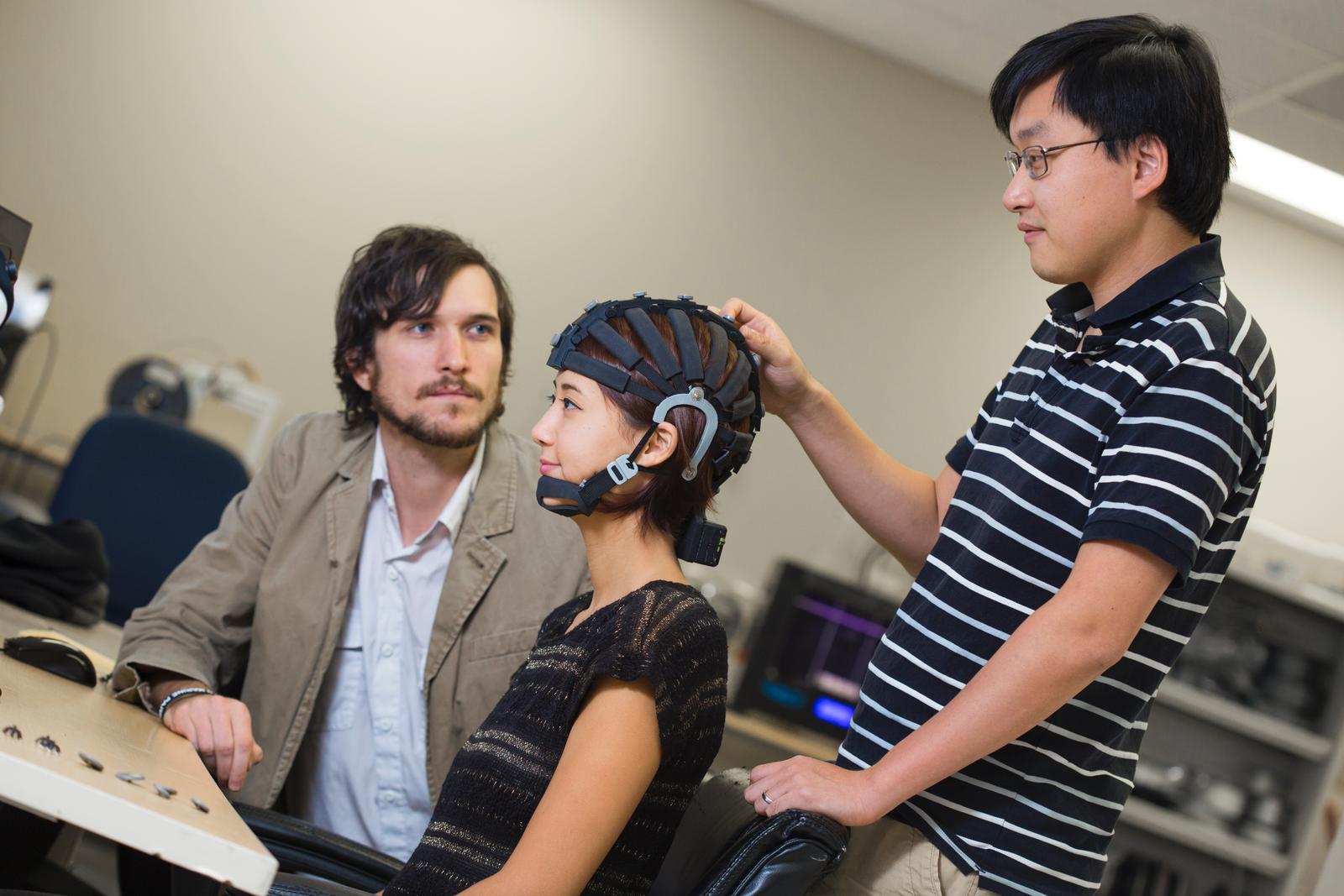
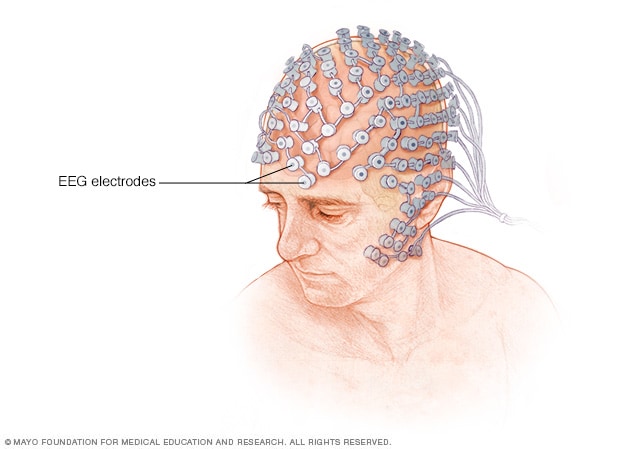
EEG is a non-invasive neuroimaging technique that records the electrical activity of the brain. It involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect and measure the electrical signals generated by brain activity. These signals, known as brainwaves, provide valuable insights into brain function, making EEG a vital tool in neuroscience, medicine, and psychology.
The Principles of EEG
Understanding the principles of EEG is crucial to grasp its significance in the field of brain research and healthcare. Here’s how it works:
- Brainwaves
The brain generates electrical signals, which are categorized into different types of brainwaves. These brainwaves include:
Delta Waves: Predominant during deep sleep.
Theta Waves: Associated with drowsiness and daydreaming.
Alpha Waves: Typically found in a relaxed but awake state.
Beta Waves: Common during alertness and cognitive tasks.
Gamma Waves: Linked to higher cognitive functions and problem-solving.
EEG records these waves, and their patterns offer valuable information about an individual’s state of consciousness and brain health.
- Electrodes
To capture brainwave activity, electrodes are strategically placed on the scalp. These electrodes are connected to an EEG device, which records and amplifies the electrical signals. The placement of electrodes can vary depending on the specific area of the brain being studied. - Amplification and Display
The electrical signals captured by the electrodes are amplified and displayed on a monitor as a continuous graph, commonly referred to as an EEG waveform. Researchers and clinicians analyze these waveforms to understand brain activity patterns and detect any irregularities. - Applications of EEG
EEG has a wide range of applications, each contributing to our understanding of the brain and its functions. Some of the key applications include:
Clinical Diagnosis: EEG is used to diagnose and monitor various neurological conditions, such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries. It helps in the assessment of brain function and the localization of abnormal activity.
Neurofeedback: In this technique, individuals can learn to control their brainwave patterns through real-time EEG feedback. It’s used to treat conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and anxiety.
Cognitive Research: EEG is a valuable tool for studying cognitive processes, such as attention, memory, and perception. Researchers use it to explore how the brain functions during specific tasks and activities.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): EEG plays a pivotal role in BCIs, enabling individuals to control external devices using their brainwaves. This technology has the potential to empower individuals with severe physical disabilities.
Mental Health: EEG is utilized in the assessment and treatment of mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety. It can help determine the effectiveness of treatments and interventions.
EEG Devices: Advancements in Brain Monitoring
The development of EEG devices has come a long way since the early days of this technology. Modern EEG devices are more sophisticated, user-friendly, and capable of delivering precise data. Here are some notable advancements in EEG technology:
- Wireless EEG Systems
Traditional EEG systems involved cumbersome wires and electrodes, which could limit a subject’s mobility. Wireless EEG systems have addressed this issue, allowing for more natural and flexible recordings. This innovation is especially valuable in research settings and for monitoring brain activity in real-world environments. - Portable EEG Devices
The portability of EEG devices has increased, making them accessible outside of traditional clinical or research settings. Portable EEG headsets are available for various applications, including neurofeedback training, gaming, and even meditation. Users can now track and train their brainwaves conveniently. - High-Density EEG
High-density EEG systems utilize a greater number of electrodes, providing a more detailed and accurate representation of brain activity. This is particularly beneficial in research where precise localization of brain functions is essential. High-density EEG has expanded our understanding of brain mapping and connectivity. - Brainwave Analysis Software
Advancements in software have simplified the analysis of EEG data. Researchers and clinicians can now process and interpret EEG waveforms more efficiently. Machine learning and artificial intelligence have also been integrated into EEG analysis, enabling the identification of subtle patterns and abnormalities.
The Future of EEG
As technology continues to evolve, the future of EEG holds even more promise. Here are some exciting developments to watch for:
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
BCIs are poised to become more sophisticated and accessible. They hold incredible potential for individuals with disabilities, allowing them to control prosthetic limbs or communicate with computers using their thoughts. This technology is likely to become more integrated into daily life. - Personalized Brain Health
Advancements in EEG may lead to personalized brain health assessments. Individuals could use portable EEG devices to monitor their brain activity and receive insights into their cognitive and emotional well-being. This information could be used to tailor lifestyle choices and mental health interventions. - Neurotherapeutics
EEG-guided neurotherapeutics may become a standard treatment for various neurological and mental health conditions. Precise brainwave targeting could lead to more effective and less invasive therapies. Neurofeedback and brainwave modulation may become mainstream approaches to improving mental well-being.
Conclusion
Electroencephalography, with its remarkable ability to decode the electrical symphony of the brain, has revolutionized our understanding of the mind. It plays a pivotal role in diagnosing neurological disorders, advancing cognitive research, and enhancing the quality of life for countless individuals. With ongoing technological advancements, EEG is set to continue unraveling the mysteries of the brain and empowering us to unlock the full potential of this incredible organ. Whether you’re a scientist, a clinician, or simply curious about the workings of the human brain, EEG is a captivating field with boundless possibilities. So, stay tuned for the exciting future of brain monitoring and research!