Introduction:
The evolution of audio technology has been nothing short of remarkable. From the humble phonograph to today’s sophisticated digital streaming services, our journey through sound has been extraordinary. We’re now entering an era where sound quality reaches new heights – the era of high-resolution audio.
As technology continues to advance, so does our ability to deliver richer, more immersive audio experiences. High-resolution audio, often referred to as hi-res audio, is at the forefront of this revolution, providing listeners with an audio quality that’s akin to being right there in the recording studio or at a live performance. In this blog post, we’ll explore what high-resolution audio is, its benefits, and how it’s changing the way we enjoy music.
What is High-Resolution Audio?
High-resolution audio is a term used to describe audio formats that offer a significantly higher level of sound quality and detail compared to standard audio formats like MP3 or CD. It’s about capturing and reproducing audio in a way that preserves every nuance, every instrument, and every note as it was intended by the artist or producer. This involves using a higher bit depth and sample rate, resulting in a more faithful representation of the original recording.
The Science Behind High-Resolution Audio:
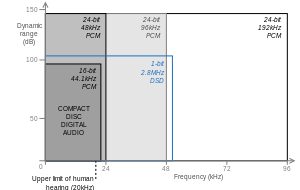
To understand the essence of high-resolution audio, it’s crucial to grasp the science that underpins it. High-resolution audio involves two key components: bit depth and sample rate.
Bit Depth: Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent each sample of audio. The higher the bit depth, the more detailed the audio. In standard audio, like CD quality (16-bit), each sample is represented with 16 bits, allowing for a range of 65,536 possible values. In high-resolution audio, 24-bit or even 32-bit bit depths are used, which translates to 16.7 million or over four billion possible values, respectively. This increased precision results in a more accurate representation of the original sound.
Sample Rate: Sample rate, measured in hertz (Hz), defines how many audio samples are taken per second to recreate sound. CDs use a 44.1 kHz sample rate, which is perfectly fine for most listeners. High-resolution audio, on the other hand, often uses sample rates of 96 kHz, 192 kHz, or even higher. This higher sample rate captures more sonic detail, especially in the high-frequency range, which might be imperceptible to the human ear but contributes to a more lifelike and immersive listening experience.
Benefits of High-Resolution Audio:
Unparalleled Sound Quality: The most apparent advantage of high-resolution audio is its unparalleled sound quality. The increased bit depth and sample rate combine to reproduce audio with exceptional fidelity, capturing every subtle nuance and timbre.
Immersion and Realism: High-resolution audio allows for a more immersive listening experience. It’s like stepping inside the music, feeling the artist’s breath and the resonance of each instrument as if you were right there during the recording or performance.
Expanded Dynamic Range: The wider dynamic range in high-resolution audio allows for both the softest and the loudest sounds to be reproduced accurately. This means you won’t miss the faintest pluck of a guitar string or the thunderous crescendo of an orchestra.
Greater Detail: High-resolution audio uncovers details that might be lost in lower-quality formats. You’ll notice the subtlest details, such as the delicate rustling of leaves in the background or the musician’s fingertips on the strings.
Audiophile Experience: High-resolution audio caters to audiophiles who demand the utmost in sound quality. It’s a treat for those with high-end audio equipment and a discerning ear.
Future-Proofing: As technology continues to evolve, high-resolution audio ensures that your music collection remains relevant and ready for the most advanced playback systems.
High-Resolution Audio Formats:
Several formats are synonymous with high-resolution audio:
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec): FLAC is a popular, open-source format that offers lossless compression. It preserves all the audio quality while reducing file sizes.
ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec): ALAC, developed by Apple, provides lossless compression and is compatible with Apple devices.
DSD (Direct Stream Digital): DSD is a format known for its extremely high sample rate (up to 11.2 MHz). It’s a favorite among audiophiles but requires specialized equipment for playback.
MQA (Master Quality Authenticated): MQA is an innovative format designed to deliver studio-quality sound in a compact file size. It’s gaining popularity for streaming high-resolution audio.
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format): WAV is a lossless audio format commonly used for high-resolution audio. It offers excellent compatibility but results in larger file sizes.
Listening to High-Resolution Audio:
To truly appreciate high-resolution audio, you’ll need the right equipment. Here’s what you’ll require:
High-Resolution Audio Files: You’ll need audio files in a high-resolution format, such as FLAC or ALAC. Many online music stores and streaming services offer high-resolution content.
High-Resolution Audio Player: Your computer, smartphone, or dedicated audio player should be capable of handling high-resolution audio files and delivering them to your headphones or speakers.
Quality Headphones or Speakers: High-resolution audio can only shine through if you have high-quality headphones or speakers capable of reproducing the finer details.
Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC): A DAC is essential to convert the digital audio signal into an analog signal that your headphones or speakers can play. Some high-end audio players have built-in DACs.
Challenges of High-Resolution Audio:
While high-resolution audio offers a remarkable listening experience, it’s not without its challenges:
Storage: High-resolution audio files are significantly larger than standard audio formats. Storing a vast library of high-resolution music can strain your storage capacity.
Compatibility: Not all devices and audio players support high-resolution audio formats. You may need to invest in specialized hardware and software for playback.
Bandwidth: Streaming high-resolution audio demands more bandwidth, which might be an issue for those with slower internet connections.
Cost: High-resolution audio files and equipment can be more expensive than standard options.
Diminishing Returns: For some listeners, the improvements in sound quality offered by high-resolution audio may not be significant enough to justify the added cost and storage requirements.
The Future of High-Resolution Audio:
As technology advances, high-resolution audio is likely to become more accessible and widespread. With the proliferation of faster internet connections and the adoption of new audio codecs, streaming high-resolution audio will become easier. More artists and recording studios are recognizing the value of high-resolution audio and are releasing their music in this format.
In conclusion, high-resolution audio represents a thrilling frontier in the world of sound. It provides an unprecedented level of detail and realism, making the listening experience more immersive and enjoyable. While there are challenges to overcome, the future of high-resolution audio looks promising, and it’s transforming the way we appreciate music. Whether you’re a discerning audiophile or simply someone who loves to savor the beauty of music, high-resolution audio is an exciting journey worth embarking upon. So, go ahead, immerse yourself in the world of high-resolution audio, and rediscover your favorite songs in a whole new light.