In today’s hyper-connected world, cybersecurity has become a paramount concern. As technology advances, so do the threats from cybercriminals. To defend against these sophisticated adversaries, organizations are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence (AI). This blog post explores the role of AI in modern cybersecurity and how it’s reshaping the digital battlefront.
The Cybersecurity Challenge
As the world becomes more interconnected, the digital domain has emerged as a battleground. From nation-states to individual hackers, cyber threats loom large, targeting everything from personal data to critical infrastructure. The traditional methods of defending against these threats are no longer sufficient. Cybersecurity requires a paradigm shift, and AI is at the forefront of this transformation.
The Power of AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing cybersecurity in several key ways:
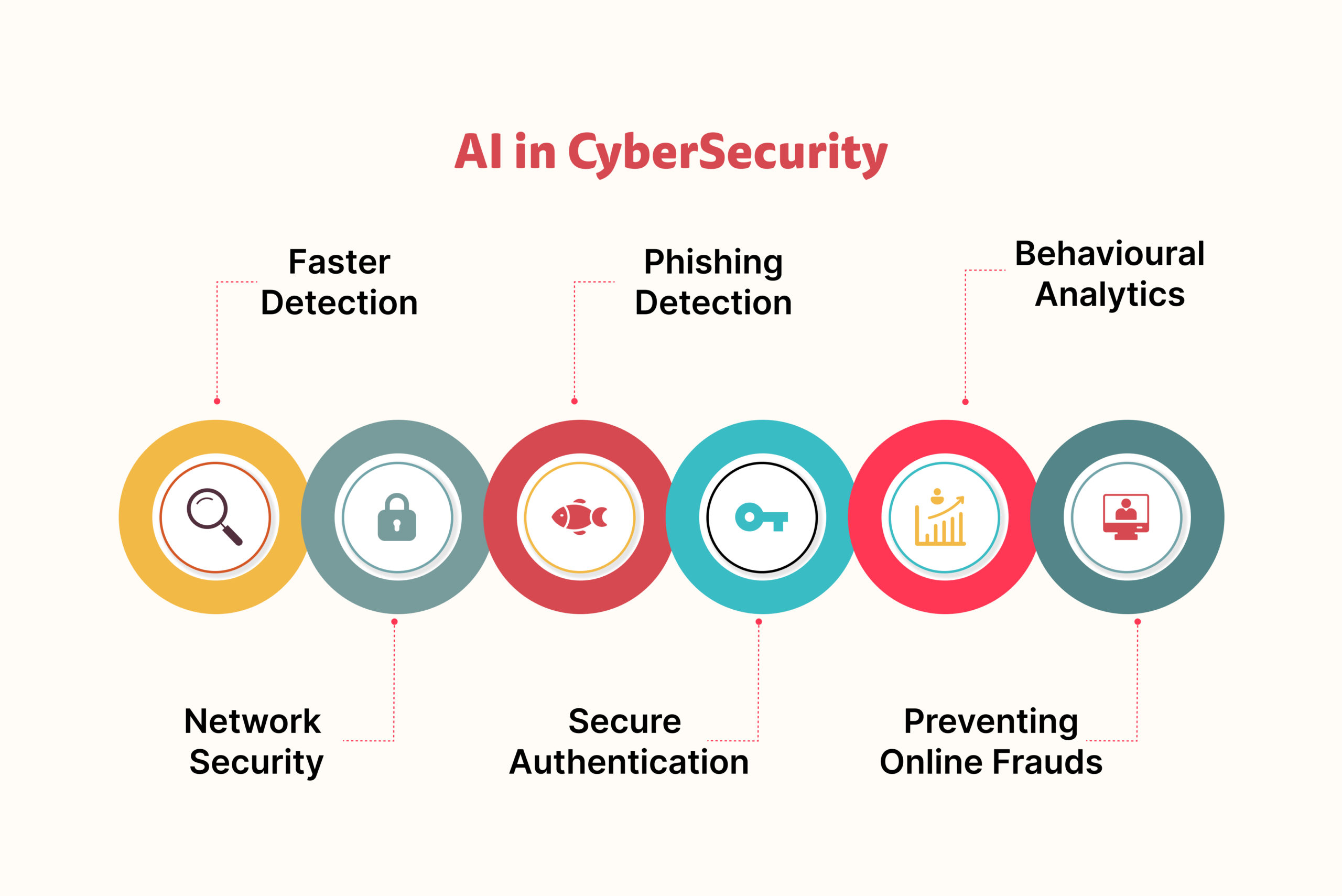
Threat Detection and Prevention: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to identify abnormal patterns and behaviors that may indicate a cyberattack. They can detect threats that would be impossible for humans to recognize quickly.
Behavioral Analysis: AI can monitor user and system behaviors continuously. It learns what normal behavior looks like and can instantly flag any deviations, potentially indicating a breach or unauthorized access.
Rapid Response: When a potential threat is identified, AI can trigger automated responses, such as isolating affected systems or blocking malicious traffic. This reduces the response time and minimizes the impact of an attack.
Predictive Analytics: AI can predict potential threats by analyzing historical data and trends. This proactive approach allows organizations to fortify their defenses before an attack occurs.
Machine Learning in Action
Machine learning, a subset of AI, plays a pivotal role in strengthening cybersecurity. Here’s how it works:
Anomaly Detection: Machine learning models can identify unusual patterns in network traffic, user behavior, or system logs. When these patterns deviate from the norm, it raises an alert for further investigation.
Zero-Day Threats: Traditional security systems may struggle to detect zero-day threats—attacks that exploit vulnerabilities unknown to the software vendor. Machine learning models can detect such threats by recognizing unusual activity.
Fraud Detection: In the realm of financial cybersecurity, machine learning is used to detect fraudulent transactions by identifying unusual spending patterns or account access.
Phishing Detection: Machine learning algorithms can analyze email content and sender behavior to flag potential phishing attempts, protecting users from falling victim to scams.
Challenges in AI-Powered Cybersecurity
While AI offers immense promise in the realm of cybersecurity, it also presents its own set of challenges and considerations:
Adversarial Attacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly using AI themselves to launch more sophisticated attacks. This includes creating AI-generated phishing emails and attempting to fool AI-based security systems.
Data Privacy: AI systems require access to large datasets for training, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting this data is crucial to prevent it from falling into the wrong hands.
Bias and Fairness: AI algorithms may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the data they are trained on. Ensuring fairness in AI cybersecurity is essential to avoid discriminatory outcomes.
Regulation and Compliance: As AI becomes a more integral part of cybersecurity, regulations and compliance standards will need to evolve to address the unique challenges posed by AI-powered systems.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
The future of AI in cybersecurity holds exciting possibilities:
Autonomous Cybersecurity: AI systems will become more autonomous, capable of making real-time decisions and responding to threats without human intervention.
Enhanced Threat Intelligence: AI will enable the development of more sophisticated threat intelligence platforms that can predict and prevent attacks on a global scale.
Collaborative Defense: AI systems from different organizations may collaborate to create a collective defense against cyber threats, sharing information and insights in real-time.
Human-AI Collaboration: Humans and AI will work together in a symbiotic relationship, with AI systems providing insights and recommendations to human cybersecurity professionals.
Conclusion
In the digital age, cybersecurity is a constant battle, and the adversaries are relentless. However, AI-powered cybersecurity provides a formidable defense, allowing organizations to stay one step ahead of cyber threats. As AI continues to evolve and adapt, it will become an indispensable tool in safeguarding our digital world. Embracing AI in cybersecurity is not just a choice; it’s a necessity to protect our data, infrastructure, and privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.