Introduction
Agriculture has been the backbone of human civilization for thousands of years, but it’s an industry that is not immune to change. In recent years, automation in agriculture has been on the rise, driven by technological advancements and the need to meet the growing global demand for food. Farmers are now leveraging automation to optimize their processes, reduce reliance on manual labor, and increase the efficiency of their operations.
This technological revolution in agriculture brings with it a set of challenges and opportunities. In this blog post, we will explore the various aspects of automation in agriculture, focusing on the cost-benefit analysis. We’ll take a closer look at the advantages of farming automation, the challenges it presents, and how to strike a balance between the two.
Advantages of Farming Automation
- Increased Efficiency One of the primary advantages of farming automation is the significant boost in efficiency. Automated machinery and systems can perform tasks with precision and consistency, reducing human errors and increasing the overall productivity of farms. For example, automated planting and harvesting equipment can cover large areas quickly and accurately, resulting in higher crop yields and reduced wastage.
- Labor Savings Automation in agriculture can lead to substantial labor savings. With the availability of autonomous tractors, drones, and robotic systems, farmers can reduce their reliance on human labor for tasks like weeding, monitoring crops, and even harvesting. This not only lowers labor costs but also addresses the challenge of labor shortages in the agricultural sector.
- Precision Farming Automation enables precision farming practices, where farmers can monitor their crops at a micro-level. Sensors and data analytics can provide insights into soil health, moisture levels, and crop conditions, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions. This results in better resource management and more sustainable farming practices.
- Increased Crop Yields By automating various aspects of agriculture, farmers can optimize their processes and enhance crop yields. Automated irrigation systems can ensure that crops receive the right amount of water, while drones can provide real-time data on crop health. These advancements lead to healthier crops and increased harvests, ultimately improving the bottom line for farmers.
Challenges of Farming Automation
- Initial Investment One of the primary challenges of adopting farming automation is the significant initial investment required. High-quality automated equipment and systems come with a substantial price tag. Farmers need to carefully weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits. This can be a barrier for small-scale and resource-constrained farmers.
- Technical Knowledge Effective implementation of automation in agriculture often requires a good understanding of technology. Farmers need to learn how to operate, maintain, and troubleshoot automated equipment and software. This can be a steep learning curve for those who are not tech-savvy, potentially leading to inefficiencies and costly mistakes.
- Maintenance and Repairs Like any machinery, automated farming equipment requires regular maintenance and occasional repairs. Ensuring the proper functioning of automated systems is crucial for uninterrupted operations. The cost of maintenance and the availability of technical support can be ongoing concerns for farmers.
- Dependence on Technology While automation offers numerous benefits, it also introduces a new set of dependencies. Farms relying heavily on technology may be vulnerable to disruptions caused by power outages, software glitches, or equipment breakdowns. Maintaining a balance between manual and automated processes is essential to ensure business continuity.
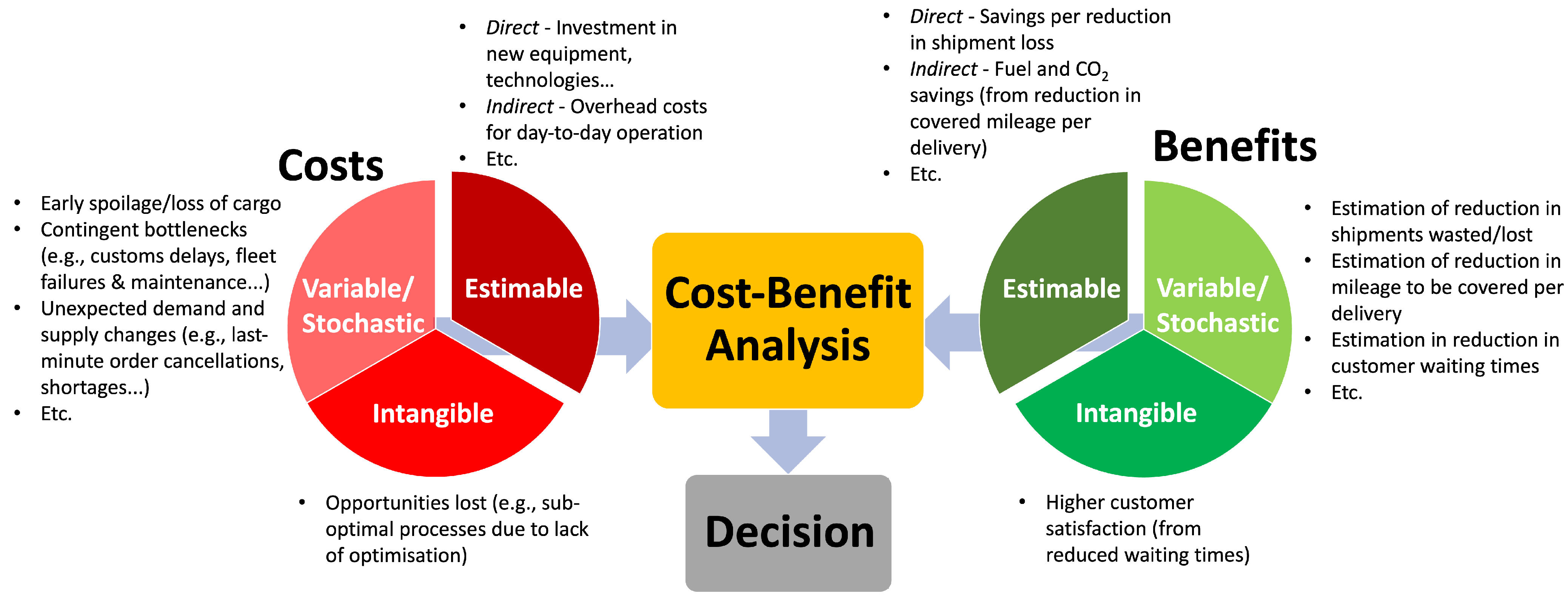
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
Balancing the advantages and challenges of farming automation requires a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Return on Investment (ROI) Farmers need to assess the expected return on investment for adopting automation. This involves calculating the potential increase in crop yields, labor savings, and operational efficiency. While the initial investment may be substantial, the long-term benefits can outweigh the costs.
- Scalability The scalability of automation solutions is a critical factor. Farmers should choose technologies that can adapt to their specific needs and growth plans. A flexible approach allows for incremental adoption of automation as resources become available.
- Training and Education Investing in training and education for both farmers and farm workers is essential to maximize the benefits of automation. Knowledge and skills development can help mitigate the challenges related to technical knowledge and equipment operation.
- Risk Mitigation Farmers should have contingency plans in place to mitigate the risks associated with automation. This includes having backup equipment, access to technical support, and strategies for dealing with unexpected challenges.
Conclusion
Automation in agriculture presents a promising future for the industry. The advantages, including increased efficiency, labor savings, precision farming, and higher crop yields, are undeniable. However, it’s crucial for farmers to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before embracing automation. By weighing the advantages against the challenges and making informed decisions, farmers can harness the full potential of automation while minimizing potential pitfalls.
In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, farming automation is poised to play a pivotal role in ensuring food security, sustainability, and increased profitability for farmers. As technology continues to advance, finding the right balance between automation and traditional farming practices will be key to a successful, modern agricultural industry.