Introduction
Agriculture is not only vital for feeding the growing global population but also plays a significant role in shaping our planet’s environmental health. It’s no secret that traditional farming practices have often had a negative impact on the environment, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, soil erosion, and water pollution. However, a transformative shift is taking place in the agriculture industry, driven by the adoption of automation technologies. In this blog post, we will delve into how automation is revolutionizing agriculture and, in turn, reducing its carbon footprint.
The Carbon Footprint Challenge
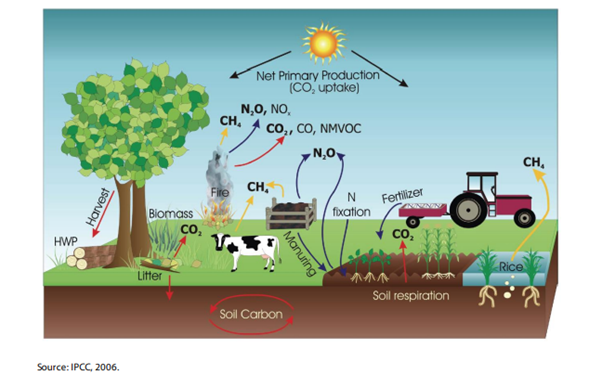
Before we explore the role of automation, it’s essential to understand the carbon footprint challenge in agriculture. Traditional farming methods are resource-intensive and often lead to emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Additionally, the extensive use of fossil fuels in agriculture, such as tractors and other machinery, further exacerbates the problem.
Automation in Agriculture: A Green Revolution
Precision Farming: One of the most significant advancements in agriculture automation is precision farming. This technology uses sensors, GPS, and data analytics to optimize various aspects of farming, including planting, harvesting, and irrigation. By precisely applying fertilizers and pesticides only where needed, farmers can reduce chemical usage and minimize soil degradation, thus lowering their carbon footprint.
Smart Irrigation: Water is a precious resource, and its mismanagement in agriculture can lead to water scarcity and environmental damage. Smart irrigation systems, powered by automation, ensure that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time. By preventing over-irrigation and water wastage, these systems conserve water resources and reduce energy consumption for pumping.
Autonomous Machinery: The use of autonomous machinery in agriculture is on the rise. These machines, such as driverless tractors and harvesters, are not only more efficient but also eco-friendly. They can be powered by electric or hybrid engines, reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional diesel-powered equipment.
Crop Monitoring and Management: Automation technologies enable continuous monitoring of crop health and growth. Drones and satellites equipped with cameras and sensors can provide real-time data on crop conditions. This information allows farmers to make informed decisions, optimize resource usage, and minimize environmental impact.
Reducing Food Waste with Automation
Another critical aspect of agriculture is food waste, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Automation plays a role here too. Automated sorting and packaging systems in food processing facilities help reduce food waste by ensuring that only the highest-quality produce reaches consumers. This not only reduces emissions from rotting food but also conserves resources by minimizing the need for additional production.
Challenges and Considerations
While automation holds immense promise for reducing the carbon footprint of agriculture, it’s not without challenges and considerations:
Initial Costs: The adoption of automation technologies can be expensive, especially for small-scale farmers. Governments and organizations must provide support and incentives to make these technologies accessible to all.
Data Privacy and Security: Automation relies heavily on data, and the collection of vast amounts of data raises concerns about privacy and security. It’s crucial to establish robust data protection measures in the agricultural sector.
Training and Education: Farmers need training to effectively utilize automation technologies. Educational programs and resources should be available to help them transition to automated farming practices.
Sustainability Metrics: It’s essential to develop standardized metrics to measure the environmental impact of automated farming accurately. This will allow for transparent reporting and comparisons across different farms and regions.
Conclusion
Automation is transforming agriculture and offering a promising path toward reducing its carbon footprint. From precision farming to smart irrigation systems, automation technologies are making farming more efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. However, for these benefits to be fully realized, stakeholders must address challenges related to cost, data security, education, and sustainability metrics. As we move forward, the integration of automation into agriculture will play a crucial role in achieving a more sustainable and environmentally responsible food production system.