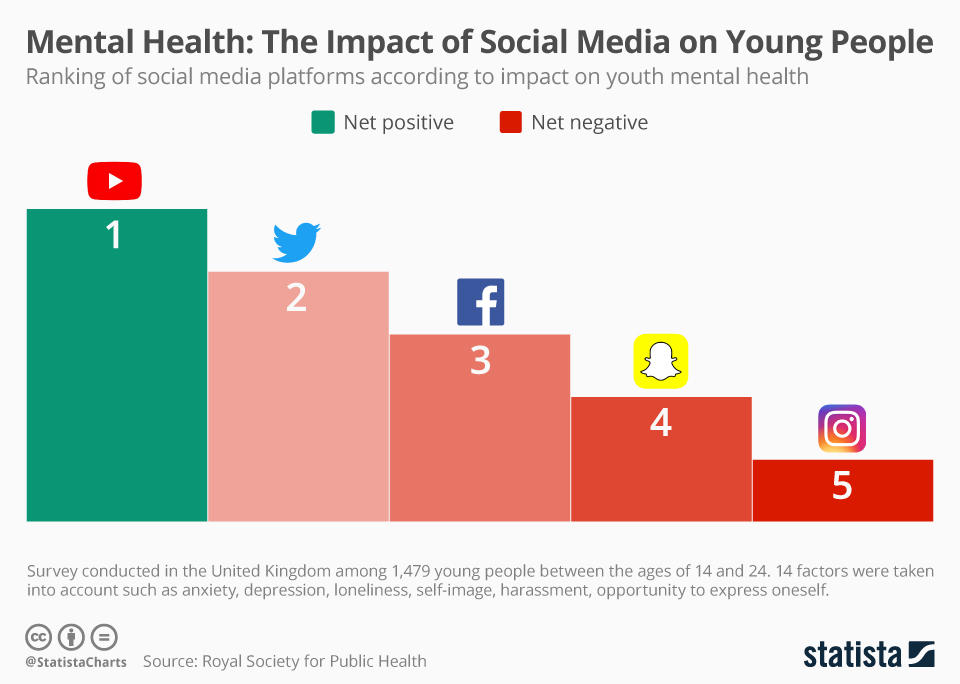
Introduction
Mental health is a topic of growing concern in our modern society. As we grapple with the demands of daily life, stressors, and various challenges, it’s becoming increasingly crucial to explore holistic approaches to maintaining and improving our mental well-being. One such approach that often gets overlooked is nutrition. The foods we eat play a vital role in shaping our mental health, and in this article, we’ll delve into the intricate connection between the two.
The Brain-Food Connection
It’s no secret that a balanced diet is essential for our physical health. We’re often reminded to consume a variety of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to maintain our bodies. But what about our brains? The brain is a highly complex organ, and it requires specific nutrients to function optimally. Let’s take a closer look at some key nutrients that play a crucial role in mental health:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They also support brain health by improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of depression and anxiety.
B Vitamins:
B vitamins, including B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for brain health. They play a role in neurotransmitter production, helping to regulate mood and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Antioxidants:
Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, as well as selenium and zinc, help protect the brain from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress has been linked to various mental health disorders, including depression and schizophrenia.
Amino Acids:
Amino acids are the building blocks of neurotransmitters, which are crucial for communication between brain cells. Consuming adequate protein in your diet ensures a steady supply of amino acids, supporting mood regulation.
The Gut-Brain Connection
In recent years, researchers have uncovered a fascinating link between the gut and the brain. The gut-brain connection, often referred to as the “second brain,” highlights the influence of our digestive system on our mental health. This connection is primarily mediated by the gut microbiome, a vast ecosystem of microorganisms that reside in our intestines.
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and the production of various compounds that impact brain function. Imbalances in the gut microbiome, often caused by a poor diet high in processed foods and sugar, can lead to inflammation and affect neurotransmitter production, contributing to mood disorders.
The Impact of Diet on Mental Disorders
Now that we’ve established the importance of nutrition in maintaining a healthy brain, let’s explore how dietary choices can impact specific mental health disorders:
Depression and Anxiety:
Numerous studies have shown that individuals who follow a Mediterranean-style diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, are less likely to experience depression and anxiety. This diet provides a wealth of nutrients that support brain health and reduce inflammation.
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder):
Children and adults with ADHD may benefit from diets high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in artificial additives and processed foods. These dietary changes can help improve focus and reduce hyperactivity.
Schizophrenia:
Some research suggests that a gluten-free, casein-free diet may be beneficial for individuals with schizophrenia. These dietary modifications can help reduce inflammation and improve symptom management.
Bipolar Disorder:
Balancing blood sugar levels through a stable, low-glycemic diet can be crucial for individuals with bipolar disorder. It helps regulate mood swings and reduce the risk of manic episodes.
Practical Steps to Improve Mental Health Through Nutrition
Now that we understand the significance of nutrition in mental health, let’s explore some practical steps to incorporate a brain-boosting diet into your daily life:
Prioritize Whole Foods:
Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods in your diet. These include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize your consumption of sugary snacks, processed foods, and sugary beverages.
Omega-3-Rich Foods:
Incorporate omega-3-rich foods like salmon, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts into your meals regularly.
Nutrient-Dense Snacks:
Choose nutrient-dense snacks such as mixed nuts, yogurt with berries, or sliced vegetables with hummus to support cognitive function throughout the day.
Stay Hydrated:
Dehydration can negatively impact mood and cognitive function. Ensure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day.
Limit Sugar and Artificial Additives:
Reduce your intake of added sugars and artificial additives, which can contribute to inflammation and mood swings.
Consult a Registered Dietitian:
If you’re unsure about the dietary changes that would benefit you most, consider consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist. They can provide personalized guidance based on your unique needs.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a profound role in our mental health, influencing our mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being. By making conscious dietary choices and prioritizing brain-boosting foods, we can take significant steps toward improving our mental health. Remember that a healthy mind begins with a well-nourished body, and by nurturing both, we can achieve a greater sense of balance and happiness in our lives.