Introduction
Bees are often seen as small, buzzing insects that we occasionally encounter while enjoying the outdoors. However, these seemingly insignificant creatures play a monumental role in agriculture and our food system. The humble bee is not just a symbol of summer but an essential partner in the process of pollination, which allows many of the crops we depend on to flourish. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the vital role of bees in agriculture and the broader ecosystem.
The Buzz about Bees
Bees are among the most well-known pollinators, and for a good reason. They are efficient and effective at transferring pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the fertilization of plants. This process is essential for the reproduction of many flowering plants, including numerous crops that make up a significant portion of our diets.
Types of Bees
Before diving into the role of bees in agriculture, it’s important to note that not all bees are created equal. There are over 20,000 known species of bees worldwide, but honeybees and bumblebees are the most recognized for their pollination services.
Honeybees: Honeybees are social insects that live in colonies. They are excellent pollinators for a wide range of crops, including apples, almonds, and blueberries. Beekeepers manage honeybee hives, which are transported to various farms to aid in pollination during the blooming season.
Bumblebees: Bumblebees are known for their distinctive buzzing sound and ability to fly in colder temperatures and lower light conditions. They are particularly effective at pollinating crops like tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries.
The Pollination Process
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male part of a flower (the anther) to the female part (the stigma) of the same or a different flower. This transfer is crucial for the fertilization of the plant, which eventually leads to the development of fruits, seeds, and vegetables.
The process of pollination occurs when bees visit flowers in search of nectar and pollen to feed themselves and their colonies. As they move from flower to flower, they inadvertently pick up and deposit pollen, facilitating the reproductive cycle of plants.
Why Bees Matter in Agriculture
The importance of bees in agriculture cannot be overstated. Here are several reasons why they are irreplaceable in this context:
Crop Diversity: Bees contribute to the cultivation of a wide variety of crops, from apples to zucchinis. Their pollination services increase crop diversity, making our diets more nutritious and enjoyable.
Higher Yields: When bees are present, crops typically yield more fruit or vegetables per plant. This increased productivity benefits both farmers and consumers.
Economic Impact: Pollinators, including bees, contribute significantly to the global economy. The economic value of bee-pollinated crops is estimated to be in the billions of dollars annually.
Environmental Stewardship: Bees also play a role in maintaining the biodiversity of wild plants, which in turn supports a range of wildlife. Their presence is a marker of a healthy ecosystem.
Resilience to Climate Change: Bees can help mitigate the impacts of climate change on agriculture. As weather patterns become more unpredictable, the reliable pollination services provided by bees become even more critical.
Challenges Facing Bees
While bees are incredibly beneficial to agriculture, they face numerous challenges that threaten their populations. These challenges include:
Pesticides: The use of pesticides, particularly neonicotinoids, has been linked to bee declines. These chemicals can harm bees’ ability to navigate, forage, and reproduce.
Habitat Loss: Urbanization and agricultural expansion have led to the destruction of bee habitats, reducing the availability of food and nesting sites.
Climate Change: Changing climate patterns can disrupt the timing of flowering plants, making it harder for bees to find food.
Diseases and Parasites: Bees are susceptible to various diseases and parasites, which can weaken and kill colonies.
Monoculture Farming: Large-scale monoculture farming reduces the availability of diverse food sources for bees and increases their vulnerability to pests and diseases.
What Can We Do to Help Bees?
Thankfully, there are steps we can take to support bee populations and ensure their continued contribution to agriculture:
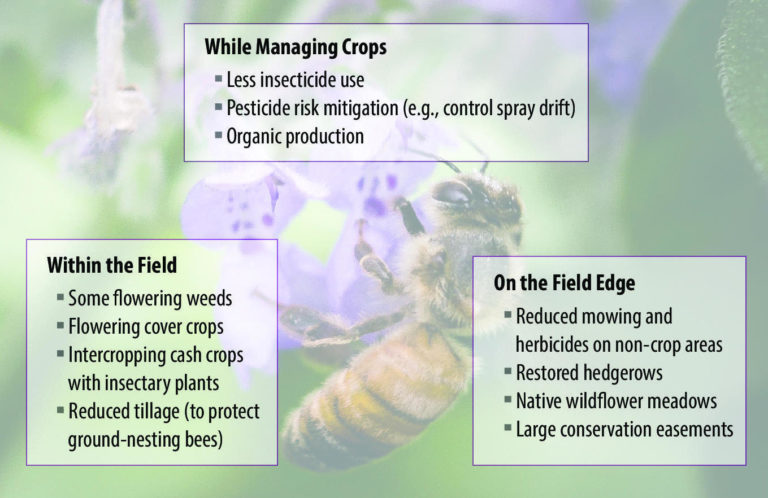
Reduce Pesticide Use: Farmers can adopt pesticide-free or integrated pest management practices to minimize harm to bees.
Create Bee-Friendly Habitats: Planting wildflowers and native plants in gardens and on farms provides bees with essential forage and nesting sites.
Support Local Beekeepers: Buying honey and other bee-related products from local beekeepers helps sustain beekeeping operations.
Educate Ourselves: Learning about the importance of bees and sharing that knowledge with others raises awareness and encourages action.
Policy Advocacy: Supporting policies and regulations that protect bee populations is crucial for their long-term survival.
Conclusion
Bees are unsung heroes of agriculture, silently working to ensure the availability of the foods we love and need. Their contribution to our food system is immeasurable, and it’s our responsibility to protect them. By taking action to support bee populations, we can ensure a thriving agricultural ecosystem and a more sustainable future for ourselves and the planet.
In this blog post, we’ve explored the indispensable role of bees in agriculture and the broader ecosystem. From their efficient pollination services to the challenges they face, it’s clear that bees are vital to our food system. By taking steps to protect and support bee populations, we can ensure a healthier and more sustainable future for agriculture and the planet as a whole.