Introduction
Agriculture is the backbone of our civilization, providing us with food, fiber, and countless other resources. However, the agricultural industry generates a significant amount of waste, and how we manage this waste can have profound implications for the environment, public health, and the sustainability of our food systems. In this blog post, we will explore the best practices for agricultural waste management, highlighting innovative solutions that are not only eco-friendly but also economically advantageous for farmers.
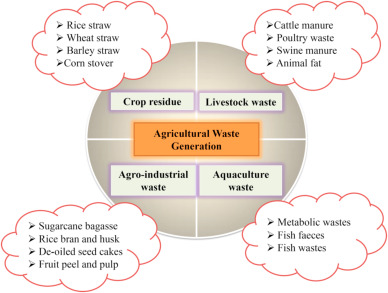
The Growing Problem of Agricultural Waste
Before delving into best practices, it’s crucial to understand the scope of the agricultural waste issue. Agricultural waste includes a wide range of materials such as crop residues, manure, agricultural plastics, and agrochemical containers. Improper disposal of these materials can lead to soil and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and a host of other environmental problems.
Moreover, the mismanagement of agricultural waste can harm human health. For instance, the burning of crop residues can release harmful air pollutants that contribute to respiratory diseases. This highlights the urgent need for responsible waste management practices in agriculture.
Best Practices for Agricultural Waste Management
Composting: Composting is a natural process that transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich compost. Farmers can compost crop residues, kitchen scraps, and manure to create a valuable soil conditioner. This not only reduces the volume of waste but also improves soil health and fertility. Composting also sequesters carbon in the soil, mitigating climate change.
Biogas Production: Biogas is a renewable energy source produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic materials, such as manure and crop residues. It can be used for electricity generation, heating, or even as a clean cooking fuel. By harnessing biogas, farmers can reduce methane emissions from manure and derive energy benefits from their waste.
Recycling Agricultural Plastics: The use of plastic materials in agriculture, such as mulch films and irrigation tubing, has increased efficiency but also led to plastic pollution. Farmers can adopt recycling programs to collect and recycle these plastics, reducing their environmental footprint.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM is a holistic approach to pest management that reduces the need for chemical pesticides. By implementing IPM practices, farmers can minimize the use of harmful chemicals, decreasing the environmental impact associated with pesticide waste.
Crop Rotation and Cover Cropping: Crop rotation and cover cropping are techniques that improve soil health and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. This not only decreases waste in the form of packaging but also prevents the accumulation of chemical residues in the environment.
Efficient Water Management: Water is a precious resource, and efficient water management practices can reduce water wastage in agriculture. Implementing drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and proper drainage systems can minimize water-related waste.
Educational Initiatives: Farmers can benefit from education and training programs on waste management best practices. Government agencies, non-profit organizations, and agricultural extension services can play a crucial role in disseminating knowledge and providing resources to farmers.
Conclusion
Agricultural waste management is a pressing issue that requires the collective effort of farmers, policymakers, and society as a whole. By adopting best practices such as composting, biogas production, recycling, and integrated pest management, farmers can minimize their environmental impact while also reaping economic benefits. Responsible waste management in agriculture is not only a sustainable choice but also a step towards safeguarding our planet for future generations.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue researching and developing innovative waste management solutions that further reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture. By doing so, we can ensure a more sustainable and prosperous future for agriculture and the planet.