Introduction:
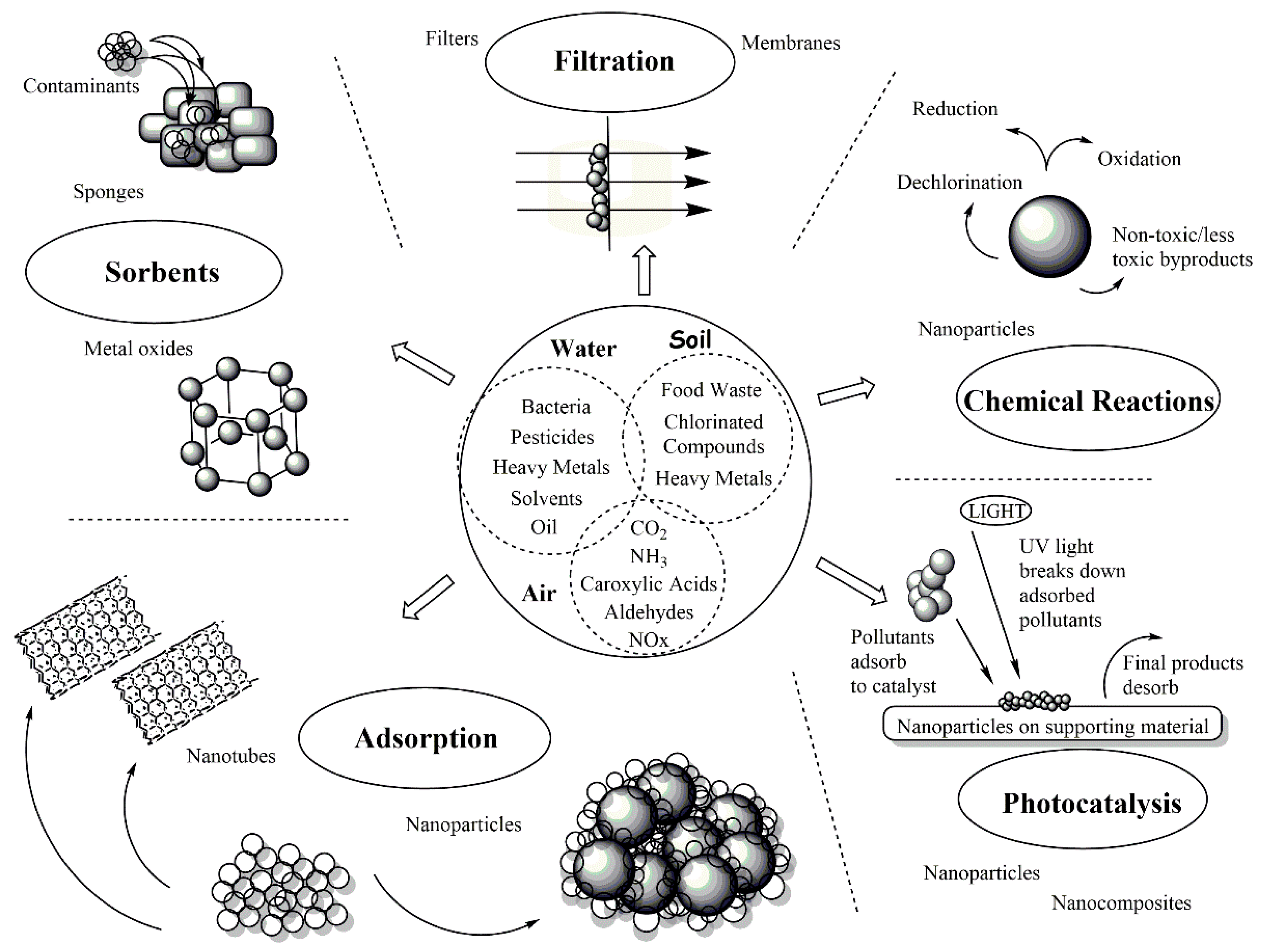
Environmental remediation is a critical field of study that focuses on cleaning up contaminated sites and restoring the health of ecosystems. Whether it’s soil, water, or air, pollution and contamination pose significant threats to the environment and human health. Traditional methods of remediation, such as excavation and chemical treatment, can be costly and time-consuming, and may not always be effective. That’s where nanotechnology comes in – by leveraging the unique properties of materials at the nanoscale, researchers are developing new tools and methods for environmental remediation that offer greater efficiency, precision, and effectiveness. In this blog post, we’ll explore the use of nanotechnology in environmental remediation and examine some of the exciting developments and applications in this field.
Nanoparticles for Pollution Removal:
One of the most promising applications of nanotechnology in environmental remediation is the use of nanoparticles for pollution removal. Nanoparticles are tiny particles that can be engineered to have specific properties, such as high surface area, reactivity, and selectivity. These properties make them ideal for removing pollutants from water, soil, and air. For example, nanoparticles of iron, titanium, and other metals can be used to break down and remove organic contaminants such as pesticides and herbicides from groundwater. Similarly, carbon-based nanoparticles such as graphene and carbon nanotubes can be used to remove heavy metals and other toxic pollutants from water.
Nanomaterials for Soil Remediation:
Another area where nanotechnology shows great promise in environmental remediation is soil remediation. Soil contamination is a significant problem worldwide, and traditional methods of remediation, such as excavation and chemical treatment, can be both costly and disruptive to the ecosystem. Nanomaterials such as nanoparticles and nanocomposites offer a more targeted and efficient approach to soil remediation. For example, nanoparticles of clay minerals such as montmorillonite and halloysite can be used to immobilize contaminants such as heavy metals and radionuclides in soil, preventing them from leaching into groundwater. Similarly, nanocomposites made of nanoparticles and polymers can be used to enhance soil microbial activity, helping to break down and remove organic contaminants.
Nanotechnology for Air Purification:
Air pollution is a major environmental problem, and traditional methods of air purification, such as filtration and scrubbing, can be expensive and energy-intensive. Nanotechnology offers a more efficient and sustainable approach to air purification by using materials with high surface area and reactivity to remove pollutants from the air. For example, nanoparticles of titanium dioxide can be used to break down pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds in the air, while carbon-based nanoparticles can be used to capture and remove particulate matter.
Conclusion:
Nanotechnology is a rapidly evolving field with enormous potential to revolutionize environmental remediation. From pollution removal to soil and air remediation, nanotechnology offers innovative solutions to some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. While there are still challenges and uncertainties to be addressed, the future looks bright for the use of nanotechnology in environmental remediation, and we can expect to see continued progress and innovation in this field in the years to come.