Cloning is a term that has been popularized in the world of science fiction. However, it is also a very real and powerful tool in biotechnology. Cloning has the potential to revolutionize many areas of biotechnology, from agriculture to medicine. However, it is also a controversial topic, with many ethical and safety concerns. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits and risks of cloning in biotechnology.
What is Cloning?
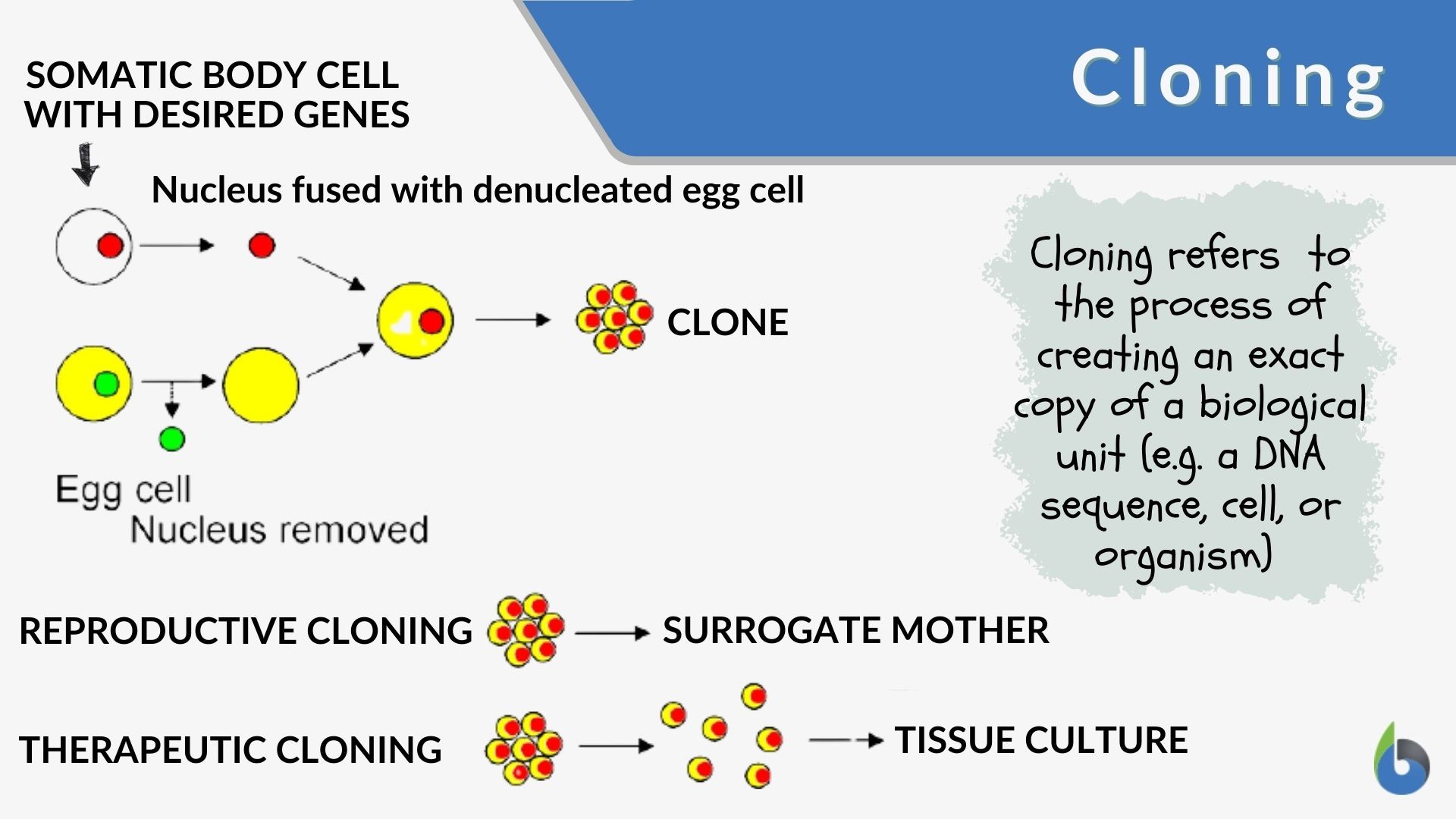
Cloning is the process of creating an exact genetic copy of an organism. In biotechnology, cloning can be accomplished through a variety of methods, including somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) and embryo splitting. SCNT involves taking the nucleus of a somatic cell (any cell that is not a sperm or egg cell) and inserting it into an enucleated egg cell. The resulting embryo is then implanted into a surrogate mother to develop into a cloned organism. Embryo splitting, on the other hand, involves splitting an early-stage embryo into multiple embryos, each of which develops into a genetically identical individual.
Benefits of Cloning in Biotechnology
Medical Research: Cloning has the potential to revolutionize medical research. By creating genetically identical animals, scientists can study the effects of diseases and treatments in a controlled environment. This can lead to the development of new treatments and cures for a variety of diseases.
Agriculture: Cloning can also be used in agriculture to produce genetically identical crops and animals with desirable traits. This can lead to increased yields, improved resistance to disease, and more efficient use of resources.
Preservation of Endangered Species: Cloning can also be used to preserve endangered species. By creating genetically identical individuals, scientists can ensure that a species is not lost to extinction.
Reproduction: Cloning can also be used to assist with reproduction in animals that have difficulty reproducing on their own. This can help to preserve valuable genetic traits in livestock and improve breeding programs.
Risks of Cloning in Biotechnology
Ethical Concerns: One of the biggest concerns with cloning is the ethical implications. The cloning of humans, for example, is widely regarded as unethical and is illegal in many countries. The cloning of animals also raises ethical concerns, particularly in terms of animal welfare.
Safety Concerns: There are also safety concerns associated with cloning. Cloned animals have been shown to have higher rates of health problems, such as cardiovascular and immune system disorders. This is thought to be due to genetic abnormalities that occur during the cloning process.
Genetic Diversity: Cloning also has the potential to reduce genetic diversity, which can have negative consequences for a species. Genetic diversity is important for a species’ ability to adapt to changing environments and resist disease.
Cost: Cloning is also a very expensive process, which limits its use in many areas of biotechnology.
Conclusion
Cloning has the potential to revolutionize many areas of biotechnology, from medicine to agriculture. However, it is also a controversial and complex topic, with many ethical and safety concerns. As technology advances, it will be important to carefully consider the benefits and risks of cloning in order to make informed decisions about its use in biotechnology.