Managing business operations is a critical aspect of running a successful company. However, companies have to make a choice between outsourcing and insourcing when it comes to their business operations. Outsourcing involves hiring an external party to perform certain tasks or operations, while insourcing refers to keeping those operations in-house. Both approaches have their advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important to consider them when deciding which approach is better for your company. In this blog post, we’ll explore the pros and cons of outsourcing and insourcing, and help you determine which approach is better for your company.
Outsourcing: Advantages and Disadvantages
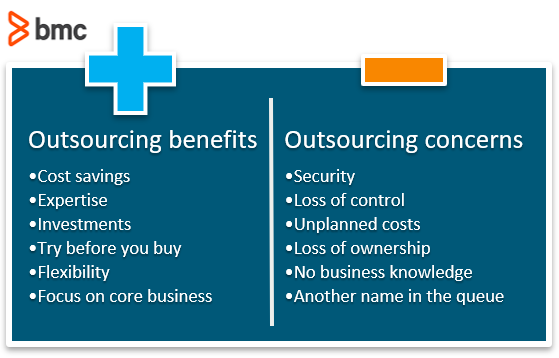
Advantages:
Cost-efficiency: Outsourcing can be cost-effective, as it eliminates the need to invest in equipment, technology, and personnel to perform the task in-house.
Access to expertise: Outsourcing enables companies to access specialized skills and knowledge that might not be available in-house.
Scalability: Outsourcing allows companies to scale their operations more easily, as they can quickly ramp up or down the size of their workforce according to their needs.
Focus on core business activities: Outsourcing frees up a company’s internal resources to focus on core business activities.
Disadvantages:
Lack of control: Outsourcing can lead to a loss of control over the operations being outsourced, which can lead to quality issues.
Communication challenges: Communication can be challenging when working with an external party, which can impact the quality of the work being performed.
Security concerns: Outsourcing can pose a security risk, as sensitive information may be shared with an external party.
Insourcing: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
Greater control: Insourcing allows for greater control over the operations being performed, which can lead to higher quality work.
Better communication: Insourcing enables easier communication and collaboration among internal teams, leading to higher quality work.
Security: Insourcing ensures that sensitive information remains within the company’s control, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Employee development: Insourcing can help develop internal talent, as employees have the opportunity to learn new skills and take on new responsibilities.
Disadvantages:
Higher costs: Insourcing can be more expensive, as it requires investment in equipment, technology, and personnel.
Limited expertise: Insourcing may limit access to specialized skills and knowledge that are not available in-house.
Scalability challenges: Insourcing can be challenging when it comes to scaling operations, as it requires investment in additional resources.
Which Approach Is Better for Your Company?
The decision to outsource or insource depends on a variety of factors, including the company’s size, industry, and operations. Here are some key factors to consider when making this decision:
Cost: If cost-efficiency is a priority, outsourcing may be the better choice. However, if cost is not a significant concern, insourcing may be a better option.
Expertise: If specialized expertise is required, outsourcing may be the better option, as it provides access to external talent. If expertise is available in-house, insourcing may be a better option.
Control: If control is a priority, insourcing may be the better option, as it provides greater control over the operations being performed.
Scalability: If scalability is a priority, outsourcing may be the better option as it allows for easier ramping up or down of operations. However, if the company has the resources to invest in additional personnel and equipment, insourcing may be a viable option.
Security: If security is a significant concern, insourcing may be the better option, as it ensures that sensitive information remains within the company’s control.
Core business activities: If the company wants to focus on its core business activities, outsourcing may be the better option, as it frees up internal resources to focus on those activities.
Industry norms: It’s also important to consider industry norms and standards when making the decision to outsource or insource. For example, certain industries may require certain operations to be performed in-house due to regulations or quality standards.
Ultimately, the decision to outsource or insource should be based on a careful evaluation of the company’s priorities, resources, and operations. In some cases, a hybrid approach that combines elements of both outsourcing and insourcing may be the best option. For example, a company may choose to outsource certain tasks that require specialized expertise, while keeping other tasks in-house to maintain greater control.
Conclusion
Outsourcing and insourcing both have their advantages and disadvantages, and the decision to choose one over the other depends on a variety of factors. Companies should carefully evaluate their priorities, resources, and operations when making this decision, and consider a hybrid approach that combines elements of both outsourcing and insourcing when appropriate. By carefully considering these factors, companies can choose the approach that best supports their business goals and helps them achieve long-term success.