In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the concept of smart cities has emerged as a beacon of hope for urbanization. As our world becomes increasingly urbanized, cities are facing unprecedented challenges in managing resources, transportation, and infrastructure. To tackle these challenges efficiently, cities are turning to the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile app development. In this blog post, we will explore the integration of IoT technology into mobile apps for smart cities, unlocking a new era of urban living.
Introduction: The Rise of Smart Cities
Urbanization is a global phenomenon, with more than half of the world’s population residing in cities. While cities offer opportunities and convenience, they also come with a multitude of challenges. Issues like traffic congestion, pollution, energy consumption, and waste management have become increasingly complex, demanding innovative solutions.
Smart cities are the answer to these challenges. They leverage technology to enhance the quality of life for citizens, improve infrastructure, and promote sustainable practices. At the core of this transformation are IoT devices and mobile apps that work in synergy to create smarter, more efficient cities.
The Role of IoT in Smart Cities
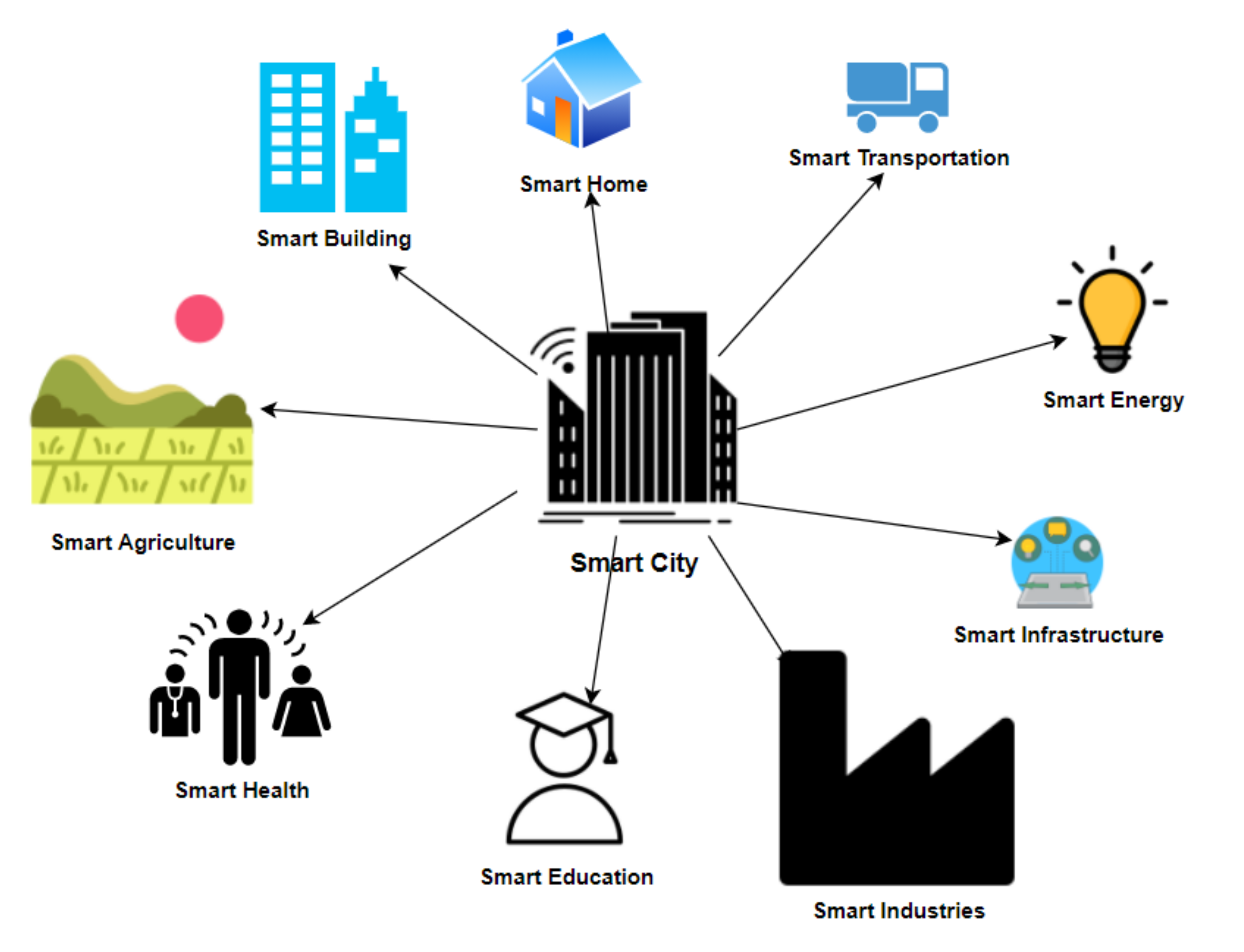
The Internet of Things, often abbreviated as IoT, refers to a network of interconnected devices and sensors that collect and exchange data over the internet. In smart cities, IoT devices are deployed across various sectors, such as transportation, energy, healthcare, and waste management. These devices continuously collect data, enabling city administrators to make data-driven decisions for efficient resource allocation and improved services.
Here are some key areas where IoT plays a crucial role in smart cities:
Smart Transportation: IoT sensors embedded in traffic lights, buses, and roads can monitor traffic flow and optimize traffic signals in real-time. Mobile apps can provide commuters with real-time updates on traffic conditions and suggest alternative routes, reducing congestion and commute times.
Energy Efficiency: IoT devices can monitor energy consumption in buildings and streetlights. Mobile apps can allow residents to control lighting and heating remotely, contributing to energy conservation and cost savings.
Waste Management: Smart waste bins equipped with IoT sensors can alert waste collection services when they are full, optimizing collection routes and reducing unnecessary pickups. Mobile apps can provide citizens with waste collection schedules and tips on reducing waste.
Public Safety: IoT-enabled surveillance cameras and sensors can enhance public safety by detecting unusual activities and incidents. Mobile apps can allow citizens to report emergencies and receive real-time alerts from law enforcement.
Building a Mobile App for Smart Cities
Mobile apps are the user-friendly interface that connects residents and city administrators with the IoT infrastructure of a smart city. These apps serve as the gateway to access real-time data, control IoT devices, and provide valuable services to citizens. Here’s how to build a mobile app for smart cities with IoT integration:
Define the App’s Purpose: Begin by identifying the specific needs of your city. What challenges are you trying to address with the app? Whether it’s improving transportation, reducing energy consumption, or enhancing public safety, a clear understanding of the app’s purpose is essential.
Select IoT Sensors: Choose the appropriate IoT sensors and devices based on the identified needs. Ensure they are compatible with the app platform and can provide real-time data.
Data Integration: Develop the backend infrastructure to collect, process, and store data from IoT devices. This may require cloud-based solutions for scalability and reliability.
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX): Design an intuitive and user-friendly interface for the mobile app. Consider the needs of both city administrators and residents. Provide interactive maps, charts, and notifications for easy access to information.
Real-Time Updates: Implement real-time data updates to keep users informed about the current state of the city. Users should have access to relevant information, such as traffic conditions, energy usage, or emergency alerts, at their fingertips.
Security: Prioritize security to protect user data and the integrity of IoT systems. Use encryption and authentication mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information.
Testing and Feedback: Thoroughly test the app to ensure its functionality and reliability. Gather feedback from users and city administrators to make improvements.
Scalability: Plan for future scalability as the city’s IoT infrastructure grows. Ensure that the app can accommodate an increasing number of devices and users.
Sustainability: Consider the environmental impact of the app and its integration with IoT devices. Strive for sustainability by promoting energy-efficient practices and reducing carbon footprint.
Education and Training: Provide training and resources for city administrators and residents to effectively use the app and IoT devices.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Smart Cities
The integration of IoT technology into mobile apps is revolutionizing the way we live in cities. As urbanization continues to rise, smart cities offer a promising solution to the challenges of resource management, traffic congestion, and environmental sustainability. By building mobile apps that harness the power of IoT, cities can create more efficient, livable, and environmentally conscious urban spaces for their residents. The future of smart cities is here, and it’s driven by innovation, connectivity, and the desire for a better quality of life.