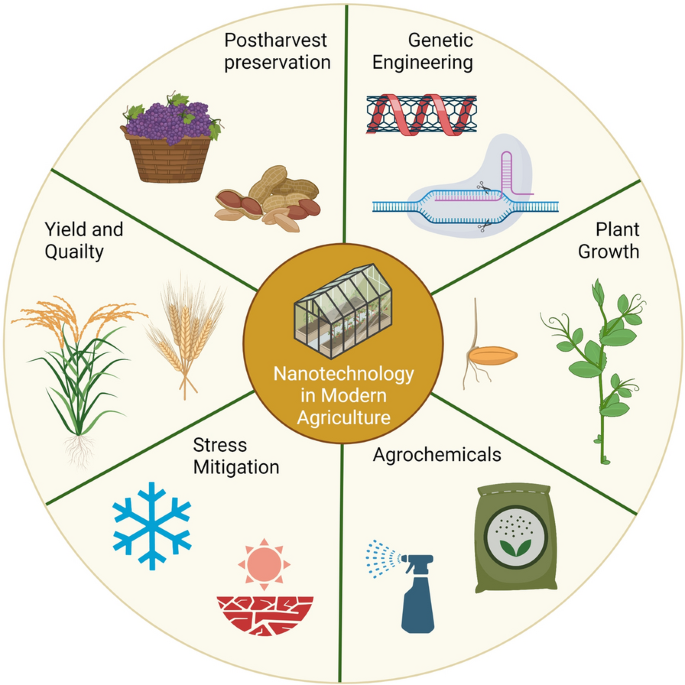
Introduction:
Agriculture has come a long way since the days of manual labor and traditional farming techniques. In the 21st century, the world faces the daunting task of feeding a growing global population while simultaneously dealing with the challenges of climate change, diminishing arable land, and the need for sustainable farming practices. Nanotechnology, with its ability to manipulate and engineer materials at the nanoscale, has emerged as a game-changer in addressing these complex issues.
Nanotechnology: A Brief Overview:
Before delving into the applications of nanotechnology in agriculture, let’s take a moment to understand what nanotechnology is. Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials and devices at the nanoscale, typically at sizes ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers. At this scale, the properties of materials can change significantly, offering unique opportunities for innovation in various fields, including agriculture.
Nanotechnology in Agriculture: A Growing Trend:
Nanotechnology has found its way into agriculture, offering a plethora of benefits that can address key challenges faced by the industry. Here are some ways in which nanotechnology is making an impact:
- Improved Nutrient Delivery:
One of the primary challenges in agriculture is ensuring that plants receive the right nutrients at the right time. Nanotechnology has facilitated the development of nanofertilizers – fertilizers with nanoparticles that release nutrients gradually, ensuring plants receive a consistent supply. This not only reduces the risk of nutrient runoff but also enhances nutrient absorption by plants, resulting in healthier and more productive crops. - Precision Agriculture:
Precision agriculture is all about optimizing resource use for maximum efficiency. Nanosensors, which are tiny devices capable of detecting and transmitting data about soil conditions, moisture levels, and nutrient content, are aiding farmers in making informed decisions. These sensors provide real-time data that allows farmers to adjust irrigation, fertilization, and pest control practices precisely, thereby minimizing waste and environmental impact. - Pest and Disease Management:
Nanotechnology has also introduced novel approaches to pest and disease management. Nanopesticides, for instance, are formulated with nanoparticles that can deliver pesticides precisely to target pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects and the environment. Additionally, nanoscale materials can be used to create barriers or coatings on plants to protect them from pathogens and environmental stressors. - Enhanced Crop Protection:
Nanomaterials such as nanoparticles of metals and metal oxides have demonstrated antimicrobial properties. These materials can be used to develop nanoscale coatings for seeds, protecting them from microbial infections during germination. This not only ensures healthier plant establishment but also reduces the need for chemical treatments. - Soil Remediation:
Nanotechnology plays a vital role in soil remediation, helping to clean up contaminated soils. Nanoparticles can adsorb and immobilize contaminants, making polluted soils safe for agriculture again. This is especially important in regions where soil pollution is a significant concern. - Controlled-Release Pesticides:
Nanotechnology has enabled the development of controlled-release pesticide formulations. These formulations release pesticides slowly over time, extending their effectiveness and reducing the need for frequent applications. This not only saves farmers money but also reduces the environmental impact of pesticide use.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
While the potential benefits of nanotechnology in agriculture are undeniable, there are also challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed. These include concerns about the safety of nanomaterials, their environmental impact, and potential unintended consequences. It is crucial for researchers, regulators, and farmers to work together to ensure that nanotechnology is deployed responsibly and with a focus on sustainability.
Conclusion:
Nanotechnology is revolutionizing the field of agriculture by offering innovative solutions to enhance crop growth and yield. From improved nutrient delivery to precision agriculture and pest management, nanotechnology is helping farmers overcome some of the most pressing challenges in modern agriculture. However, it is essential to approach nanotechnology in agriculture with caution, addressing safety and ethical considerations to ensure a sustainable and productive future for farming.
As we continue to explore the vast potential of nanotechnology in agriculture, it is clear that this technology will play a significant role in shaping the future of farming, allowing us to produce more food with fewer resources while minimizing the environmental impact. In the coming years, we can expect to see even more exciting developments as researchers and farmers harness the power of nanotechnology to feed a growing world population and build a more sustainable agricultural industry.